android->在界面上使用URI编程----开发笔记1
导言
做android 开发有一段时间了,很多时候就是做些重复性的数据绑定,还有就是不够操作不够灵活,例如,我在某个界面要新增一个按钮,就需要发布一个新版本,就这么一个按钮的话其实,可以完全由服务器控制,例如UC,凡客他们要更新首页,不可能为了更新一个首页特地开发一个新版本,那多傻啊,所以,观察了一下,想出了一个可能解决的方案…
1.控制显示
如何做到有服务器控制客户端的显示呢?
我们可以在客户端预留一些可能会用的例如UC的首页:
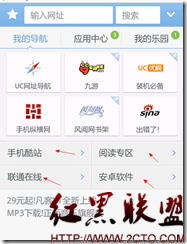
箭头标志的区域,是会根据不同情况而更新,而我现在就是要做出这样的效果.
如何控制显示?
我们知道,android 找view是通过一系列ID 值找到相关的UI 那样,我们可以通过,在服务端,发送我们要修改的id.
1,是直接发送ID值还是发送一个具体路径?
这点,我毫无犹豫的选择了发送一个ui的路径,通过在客户端把这个URI进行转义,然后获得,相关的ID值.代码
/**
* 资源ID 的几种形式
* res = package:type/entry
* 1,res://com.achai@drawable/test_icon
* 2,res://drawable/test_icon
*(1) 不带具体包名
*entry = layout/main
*(2) 指定包名和类型实体
*com.achai@drawable/icon
* @param url
* @return
*/
public static int getResIdFromURL(String url){
URI uri = URI.create(url);
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
String type = uri.getHost();
String entry = uri.getPath();
entry = entry.replaceFirst("/", "");
String packageName = uri.getUserInfo();
if(ress == null)
initRes();
if(ress == null)
return -1;
//判断是否android资源URL
if(!scheme.equals("res"))
return -1;
//1,判断是否是带包名的uri,并执行转换,获得资源ID
if(packageName != null){
return ress.getIdentifier(entry, type, packageName);
}else{
return ress.getIdentifier(entry, type, defPackage);
}
}
思路就如同代码那样,这样,我们的客户端就能够解析服务端发送过来要改哪个UI的了!接着就是修改值的事情了,这部分,以后继续!
2,控制监听
还是用uc作为例子:
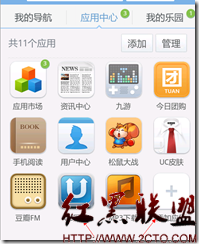
在 UC的应用中心中,有个添加应用,这里就有个问题,我们如何监听我们新增的应用呢?
x
我翻阅android api的时候发现这么一行话
Tags
Unlike IDs, tags are not used to identify views. Tags are essentially an extra piece of information that can be associated with a view. They are most often used as a convenience to store data related to views in the views themselves rather than by putting them in a separate structure.
看到这里,我觉得就可以在这里做点文章了.
我们可以做一个tag 命令系统,然后,在这些新增应用的tag上打上一个标签命令,例如,UC就可能在这些应用上的tag 打上一个url 我们点击的时候,就会跳转到相关的应用.
根据这个思路敲下如下代码
public void doViewClicked(View v){
String url = v.getTag().toString().trim();
if(v != null && url != null){
//对view 中tag 进行解析
doExecUrl(v, url);
}
}
protected void doExecUrl(View view, String url) {
try{
if(url.indexOf('\n') > 0){
String[] urls = url.split("\n");
for(String u : urls){
execUrl(view, u);
}
}else{
execUrl(view, url);
}
}catch(RuntimeException ex){
UserApp.curApp().showMessage("url 解析错误");
}
}
private void execUrl(View view, String u) {
URI execUri = URI.create(u);
if(execUri == null)
return;
String prefix = execUri.getScheme();
//执行相关的的命令 www.zzzyk.com
if(prefix.equals("cmd")){
execCmd(execUri);
}else if(prefix.equals("act")){
execAct(execUri);
}
}
/**
* 执行命令操作
* @param u
*/
private void execCmd(URI u){
String type = u.getHost();
//监控 watch
if(type.equals("watch")){
//用于观察view 中的变量改变情况,晚些在实现
return;
}
//结束当前view
if(type.equals("finish")){
theAct.finish();
return;
}
//弹出提示
if(type.equals("hint")){
String msg = u.getFragment();
if(msg != null){
UserApp.showMessage(theAct, msg);
}
return;
}
//重新读取
if(type.equals("reload")){
return;
}
//设置指定id view 的值
if(type.equals("setview")){
return;
}
//设置显示某个view
if(type.equals("showview")){
return;
}
}
这样,我们可以在初始化view的时候,遍历所有view的元素,有tag命令就设置监听器!
public void checkView(){
ViewGroup vg = (ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.line);
int count = vg.getChildCount();
for(int i=0; i < count; i ++){
View child = vg.getChildAt(i);
String tag = (String) child.getTag();
if(tag != null){
initTagCmd.setViewTagListenr(child);
}
}
}
这样我们就可以很灵活的操作我们的UI 事件了!
k
可能有人会说效率问题?
效率的影响那是肯定会有的,但是,你想一下,一个view 官方推荐不要超过80个,一般而言也就10来个,遍历消耗的时间估计就算是htc g1(第一台android手机)那样的配置的手机都没问题,更何况是现在4核的android手机….
试一下效果:
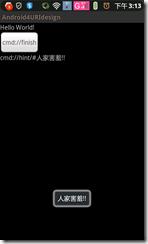
这是一个开源的玩意…
这个项目放在了github上,如果有朋友,想试一下可以到以下链接下载或者关注,提供一些建议,完善的话会慢慢来…
摘自 youxiachai
补充:移动开发 , Android ,