trie树(字典树)
一:Trie的简单实现(插入、查询)Trie,又称字典树、单词查找树,是一种树形结构,用于保存大量的字符串。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间。
1
2#include <iostream>
3using namespace std;
4
5const int branchNum = 26; //声明常量
6int i;
7
8struct Trie_node
9{
10 bool isStr; //记录此处是否构成一个串。
11 Trie_node *next[branchNum];//指向各个子树的指针,下标0-25代表26字符
12 Trie_node():isStr(false)
13 {
14 memset(next,NULL,sizeof(next));
15 }
16};
17
18class Trie
19{
20public:
21 Trie();
22 void insert(const char* word);
23 bool search(char* word);
24 void deleteTrie(Trie_node *root);
25private:
26 Trie_node* root;
27};
28
29Trie::Trie()
30{
31 root = new Trie_node();
32}
33
34void Trie::insert(const char* word)
35{
36 Trie_node *location = root;
37 while(*word)
38 {
39 if(location->next[*word-'a'] == NULL)//不存在则建立
40 {
41 Trie_node *tmp = new Trie_node();
42 location->next[*word-'a'] = tmp;
43 }
44 location = location->next[*word-'a']; //每插入一步,相当于有一个新串经过,指针要向下移动
45 word++;
46 }
47 location->isStr = true; //到达尾部,标记一个串
48}
49
50bool Trie::search(char *word)
51{
52 Trie_node *location = root;
53 while(*word && location)
54 {
55 location = location->next[*word-'a'];
56 word++;
57 }
58 return(location!=NULL && location->isStr);
59}
60
61void Trie::deleteTrie(Trie_node *root)
62{
63 for(i = 0; i < branchNum; i++)
64 {
65 if(root->next[i] != NULL)
66 {
67 deleteTrie(root->next[i]);
68 }
69 }
70 delete root;
71}
72
73void main() //简单测试
74{
75 Trie t;
76 t.insert("a");
77 t.insert("abandon");
78 char * c = "abandoned";
79 t.insert(c);
80 t.insert("abashed");
81 if(t.search("abashed"))
82 printf("true\n");
83}
二:下面是另外的一种实现
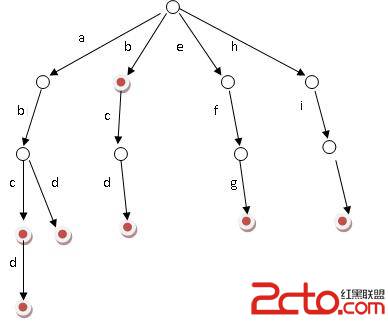
Trie,又称字典树、单词查找树,是一种树形结构,用于保存大量的字符串。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间。相对来说,Trie树是一种比较简单的数据结构.理解起来比较简单,正所谓简单的东西也得付出代价.故Trie树也有它的缺点,Trie树的内存消耗非常大.当然,或许用左儿子右兄弟的方法建树的话,可能会好点.
其基本性质可以归纳为:
1. 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
2. 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
3. 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
其基本操作有:查找 插入和删除,当然删除操作比较少见.我在这里只是实现了对整个树的删除操作,至于单个word的删除操作也很简单.
搜索字典项目的方法为:
(1) 从根结点开始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找关键词的第一个字母,并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索;
(3) 在相应的子树上,取得要查找关键词的第二个字母,并进一步选择对应的子树进行检索。
(4) 迭代过程……
(5) 在某个结点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该结点上的信息,即完成查找。
其他操作类似处理.
/*
Name: Trie树的基本实现
Author: MaiK
Description: Trie树的基本实现 ,包括查找 插入和删除操作(卫星数据可以因情况而异)
*/
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int sonnum=26,base='a';
struct Trie
{
int num;//to remember how many word can reach here,that is to say,prefix
bool terminal;//If terminal==true ,the current point has no following point
struct Trie *son[sonnum];//the following point
};
Trie *NewTrie()// create a new node
{
Trie *temp=new Trie;
temp->num=1;temp->terminal=false;
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)temp->son[i]=NULL;
return temp;
}
void Insert(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)// insert a new word to Trie tree
{
Trie *temp=pnt;
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
{
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]==NULL)temp->son[s[i]-base]=NewTrie();
else temp->son[s[i]-base]->num++;
temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
}
temp->terminal=true;
}
void Delete(Trie *pnt)// delete the whole tree
{
if(pnt!=NULL)
{
for(int i=0;i<sonnum;++i)if(pnt->son[i]!=NULL)Delete(pnt->son[i]);
delete pnt;
pnt=NULL;
}
}
Trie* Find(Trie *pnt,char *s,int len)//trie to find the current word
{
Trie *temp=pnt;
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
if(temp->son[s[i]-base]!=NULL)temp=temp->son[s[i]-base];
else return NULL;
return temp;
}
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,