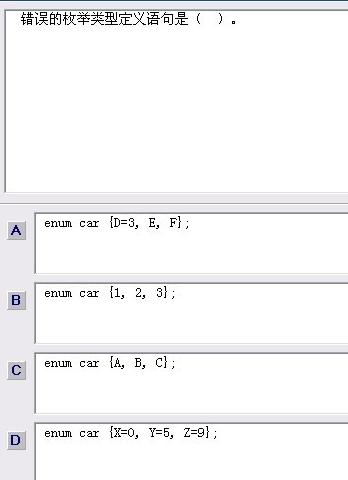
C 数据结构:树 功能:基本操作
树的定义便是递归定义,所以绝大多功能采用递归完成
001 #include <stdio.h>
002 #include <malloc.h>
003 #include <stdlib.h>
004 #define MAX 100
005 #define ERROR 0
006 #define OK 1
007 #ifndef Type
008 typedef char Type;
009 #endif
010
011 typedef struct Bitree
012 {
013 Type data;
014 struct Bitree *lchild;
015 struct Bitree *rchild;
016 }BitNode, *BiTree;
017
018 int InitBiTree(BiTree *T)//初始化空树
019 {
020 *T = NULL;
021 return OK;
022 }<SPAN style="COLOR: #e53333" minmax_bound="true">//假如传入的参数是指向BitNode的指针,也就是BiTree 由于对于树的构建是使用递归的方式,所以在对子树
023 //因为子树的类型也为BiTree 所以此时无法改变其实(传值,形参),所以参数要使用指向Bitree的指针</SPAN> /*
024 int Creat(BiTree T)
025 {
026 Type p;
027
028 scanf("%c", &p);
029
030 if (p == ' ')
031 T = NULL;
032 else
033 {
034 T->data = p;
035 T->lchild = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BitNode));
036 Creat(T->lchild);
037 T->rchild = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BitNode));
038 Creat(T->rchild);
039 }
040 return OK;
041 }
042 */
043
044 int CreatBiTree(BiTree *T)//用递归的方式创建树(前序输入,空格表示子树为空)
045 {
046 Type p;
047
048 scanf("%c", &p);
049
050 if (p == ' ')
051 *T = NULL;
052 else
053 {
054 *T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BitNode));
055 (*T)->data = p;
056 CreatBiTree(&(*T)->lchild);
057 CreatBiTree(&(*T)->rchild);
058 }
059 return OK;
060 }
061
062 int ClearBiTree(BiTree *T)//清除树,同样为递归的方式
063 {
064 if ((*T)->lchild)
065 ClearBiTree(&((*T)->lchild));
066 if ((*T)->rchild)
067 ClearBiTree(&((*T)->rchild));
068
069 if ((*T)->lchild == NULL && (*T)->rchild == NULL)
070 {
071 free(*T);
072 *T = NULL;
073 }
074 return OK;
075 }
076
077 int BiTreeEmpty(BiTree T)//判断树是否为空
078 {
079 if (T == NULL)
080 return OK;
081 return ERROR;
082 }
083
084 int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T)//树的深度
085 {
086 int hl, hr;
087 if (T == NULL)
088 return 0;
089 else
090 {
091 hl = BiTreeDepth(T->lchild);
092 hr = BiTreeDepth(T->rchild);
093 if (hl > hr)
094 return hl + 1;
095 else
096 return hr + 1;
097 }
098 }
099
100 BitNode Root(BiTree T)//返回树的根(节点)
101 {
102 if (T == NULL)
103 {
104 printf("No Root");
105 exit(0);
106 }
107 return *T;
108 }
109
110 int InserInc(BiTree *T, Type e)//按照字母序插入节点 (小于该节点的为其左子树,大于该节点的为其右子树)
111 {
112 BiTree temp;
113
114 temp = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BitNode));
115 temp->data = e;
116
117 if (*T == NULL)
118 {
119 temp->lchild = NULL;
120 temp->rchild = NULL;
121 *T = temp;
122 }
123 else
124 {
125 if (e < (*T)->data)
126 InserInc(&((*T)->lchild), e);
127 else
128 InserInc(&((*T)->rchild), e);
129 }
130 return OK;
131 }
132
133
134 BiTree Search(BiTree T, Type p)//返回值为p的节点,否则为空
135 {
136 BiTree temp;
137 if (T == NULL)
138 return ERROR;
139 else
140 {
141 if (T->data == p)
142 return T;
143 else
144 {
145 temp = Search(T->lchild, p);
146 if (temp == NULL)
147 temp = Search(T->rchild, p);
补充:软件开发 , C语言 ,