使用Python语言替代AMPL建模流程说明
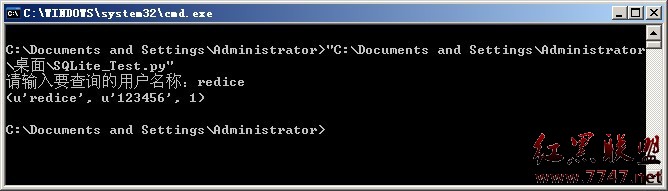
PULP是用python写的建模描述语言,自带的例子里面就带有column generation的例子,显然是比glpk自带的那个强不少,下面就用一个例子来说明一个简单建模的流程吧。Python代码
- # Import PuLP modeler functions
- from pulp import *
- # A new LP problem
- prob = LpProblem("test1", LpMinimize)
- # Variables
- # 0 <= x <= 4
- x = LpVariable("x", 0, 4)
- # -1 <= y <= 1
- y = LpVariable("y", -1, 1)
- # 0 <= z
- z = LpVariable("z", 0)
- # Use None for /- Infinity, i.e. z <= 0 -> LpVariable("z", None, 0)
- # Objective
- prob = x 4*y 9*z, "obj"
- # (the name at the end is facultative)
- # Constraints
- prob = x y <= 5, "c1"
- prob = x z >= 10, "c2"
- prob = -y z == 7, "c3"
- # (the names at the end are facultative)
- # Write the problem as an LP file
- prob.writeLP("test1.lp")
- # Solve the problem using the default solver
- prob.solve()
- # Use prob.solve(GLPK()) instead to choose GLPK as the solver
- # Use GLPK(msg = 0) to suppress GLPK messages
- # If GLPK is not in your path and you lack the pulpGLPK module,
- # replace GLPK() with GLPK("/path/")
- # Where /path/ is the path to glpsol (excluding glpsol itself).
- # If you want to use CPLEX, use CPLEX() instead of GLPK().
- # If you want to use XPRESS, use XPRESS() instead of GLPK().
- # If you want to use COIN, use COIN() instead of GLPK(). In this last case,
- # two paths may be provided (one to clp, one to cbc).
- # Print the status of the solved LP
- print "Status:", LpStatus[prob.status]
- # Print the value of the variables at the optimum
- for v in prob.variables():
- print v.name, "=", v.varValue
- # Print the value of the objective
- print "objective=", value(prob.objective)
补充:Web开发 , Python ,