C++ 基础之 "引用形参" 和 "利用const引用避免复制"
//重载操作符+
Vector3 operator+(const Vector3 &a){
return Vector3(x + a.x,y + a.y,z+a.z);
}
//比较两个数,如果相同返回0,如果v1大,返回1,如果v2大,返回-1
int compare(const int &v1, const int &v2)
{
if(v1 < v2) return -1;
if(v2 < v1) return 1;
return 0;
}
因为之前是用C#和Java比较多,就是无法理解这两个函数的参数定义,为什么要加上const和&。其实有时候看到&,*,T等符号就会头大。如果在java中第二个函数我肯定就会这样写:
//比较两个数,如果相同返回0,如果v1大,返回1,如果v2大,返回-1
int compare( int v1, int v2) www.zzzyk.com
{
if(v1 < v2) return -1;
if(v2 < v1) return 1;
return 0;
}
先不管上面的东西,再来看一个出现无数次的交换例子:
[cpp] view plaincopy
//把形参定义为引用类型
void swapOne(int& a, int& b)
{
int tmp = b;
b = a;
a = tmp;
}
//使用复制实参,只是改变局部副本,而传递函数的实参没有修改
void swapTwo(int a,int b)
{
int tmp = b;
b = a;
a = tmp;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
printf("before swap,a:%d,b:%d\n",a,b);
swapOne(a,b);
printf("after swap,a:%d,b:%d\n",a,b);
printf("before swap,a:%d,b:%d\n",a,b);
swapTwo(a,b);
printf("after swap,a:%d,b:%d\n",a,b);
return 0;
}
结果如下:
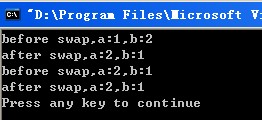
从结果看出,swapOne函数使用引用形参成功交换了a,b变量。而swapTwo函数没有交换成功。
swapTwo使用的是普通的非引用类型的参数,是通过复制对应的实参实现初始化,传递函数的实参没有改变。
而swapOne中,引用形参直接关联到其绑定的对象,而并非这些对象的副本。所以交换会成功。
[cpp] view plaincopy
//比较两个数,如果相同返回0,如果v1大,返回1,如果v2大,返回-1
int compare(const int &v1, const int &v2)
{
if(v1 < v2) return -1;
if(v2 < v1) return 1;
return 0;
}
上面这例子中的const还有什么作用呢?原来使用const可以避免引用复制,提高性能,swapOne中当然不能使用了,因为它要改变值,而compare函数只是比较两个数的大小,没有交换,所以加上const可以提高性能。因为复制对象需要付出时间和存储空间代价。
后记:最近无意中看到了《Effective C++》的条款20“宁以pass-by-reference-to-const 替换 pass-by-value”。中也谈到了这个问题。
[cpp] view plaincopy
class Person{
public:
Person();
virtual ~Person();
...
private:
std::string name;
std::string address;
};
class Student:public Person{
public:
Student();
~Student();
...
private:
std::string schoolName;
std::string schoolAddress;
}
假设现在有这样一个函数
bool validateStudent(Student s);
如果用by Value方式来调用就是
Student plato;
bool platoIsOk = validateStudent(plato);
因为Student类是继承Person类,每个类都有两个string。书上说,by value方式传递一个Student对象,总体成本是"六次构造函数和六次析构函数"!
如果改成成pass by reference-to-const:
bool validateStudent(const Student& s);没有任何构造函数或析构函数被调用,因为没有任何新对象被创建。
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,