Android ApiDemos示例解析(35):App->Preferences->Advanced preferences
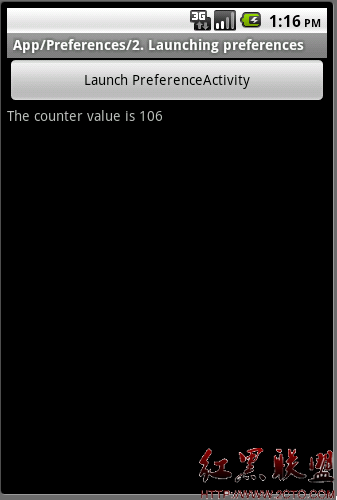
前篇文章Android ApiDemo示例解析(31):App->Preferences->Launching preferences 中用到了Advanced preferences 中定义的AdvancedPreferences。
本篇具体介绍AdvancedPreferences, 这个例子称为Advanced ,是因为它涉及到了自定义Preference, 并在一个工作线程中刷新某个Preference的值。
Preference 为显示在PreferenceActivity (一般以列表显示)在某个偏好的基类。有点类似于显示在Activity中的某个View。Preference 实际存取的是对应在Shared Preferences中一项,而Preference定义的key也就是用来访问Shared Preferences的key值。
和View一样可以自定义View,在Android中也可以自定义Preference,用来显示管理应用自定义的程序偏好。本例 MyPreference 自定义一个Preference 用来存储用户点击该Preference的次数,类型为整数,初始值定义为100。它在advanced_preferences.xml 对应的定义如下:
<com.example.android.apis.app.MyPreference
android:key=”my_preference”
android:title=”@string/title_my_preference”
android:summary=”@string/summary_my_preference”
android:defaultValue=”100″ />
Preference 定义了很多属性,比如Default Value, dependency, enabled, icon ,key 等等都有对应的方法来操作。并且提供了两个Listener:PreferenceChangeListener, PreferenceClickListener ,允许应用程序响应Preference值变化事件,或是用户点击Preference事件。
这里按照MyPreference 代码顺序说明一下如何自定义一个Preference。
1. 派生于 Preference基类。
[java]
public class MyPreference extends Preference
public class MyPreference extends Preference
2. 和自定义View类似可以为自定义Preference 自定义Layout。 MyPreference 使用R.layout.preference_widget_mypreference ,定义很简单只有一个TextView ,其id为mypreference_widget。 一般在构造函数中使用setWidgetLayoutResource为Preference派生类设置Layout资源。
[java] view plaincopyprint?
// This is the constructor called by the inflater
public MyPreference(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setWidgetLayoutResource(R.layout.preference_widget_mypreference);
}
// This is the constructor called by the inflater
public MyPreference(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setWidgetLayoutResource(R.layout.preference_widget_mypreference);
}
3. 如有需要为自定义的Layout中的View 设置属性,可以在onBindView(View view)中完成。下面代码为TextView设置值为mClickCounter。
[java]
@Override
protected void onBindView(View view) {
super.onBindView(view);
// Set our custom views inside the layout
final TextView myTextView
= (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.mypreference_widget);
if (myTextView != null) {
myTextView.setText(String.valueOf(mClickCounter));
}
}
@Override
protected void onBindView(View view) {
super.onBindView(view);
// Set our custom views inside the layout
final TextView myTextView
= (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.mypreference_widget);
if (myTextView != null) {
myTextView.setText(String.valueOf(mClickCounter));
}
}
4. 如果为该自定义Preference 在XML定义了初值,比如 MyPreference的初值android:defaultValue=”100″,我们想在代码中使用这个初值来初始化变量mClickCounter 。mClickCounter 类型为整数,这个变量就是用来保存用户的按键次数的。
[java]
@Override
protected Object onGetDefaultValue(TypedArray a, int index) {
// This preference type's value type is Integer, so we read the default
// value from the attributes as an Integer.
return a.getInteger(index, 0);
}
@Override
protected void onSetInitialValue(boolean restoreValue, Object defaultValue) {
if (restoreValue) {
// Restore state
mClickCounter = getPersistedInt(mClickCounter);
} else {
// Set state
int value = (Integer) defaultValue;
mClickCounter = value;
persistInt(value);
}
}
@Override
protected Object onGetDefaultValue(TypedArray a, int index) {
// This preference type's value type is Integer, so we read the default
// value from the attributes as an Integer.
return a.getInteger(index, 0);
}
@Override
protected void onSetInitialValue(boolean restoreValue, Object defaultValue) {
if (restoreValue) {
// Restore state
mClickCounter = getPersistedInt(mClickCounter);
} else {
// Set state
int value = (Integer) defaultValue;
mClickCounter = value;
persistInt(value);
}
}
5 重载 onSaveInstanceState,onRestoreInstanceState ,这两个方法是用来临时保存或是恢复一些变量值。在Preference 调用persistInt,persistBoolean, persistString等之前,preference 对应的值还没有被保存在或是更新在Shared preferences 中,如果这时用户旋转屏幕,则造成Activity重新创建,我们需要在屏幕旋转时用户选择项会保留,可以使用onSaveInstanceState,onRestoreInstanceState来保持一些临时数据。
[java]
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
/*
* Suppose a client uses this preference type without persisting. We
* must save the instance state so it is able to, for example, survive
* orientation changes.
*/
final Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
if (isPersistent()) {
// No need to save instance state since it's persistent
return superState;
}
// Save the instance state
final SavedState myState = new SavedState(superState);
myState.clickCounter = mClickCounter;
return myState;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (!state.getClass().equals(SavedState.class)) {
// Didn't save state for us in onSaveInstanceState
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
return;
}
// Restore the instance state
SavedState myState = (SavedState) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(myState.getSuperState());
mClickCounter = myState.clickCounter;
notifyChanged();
}
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
/*
* Suppose a client uses this preference type without persisting. We
* must save the instance state so it is able to, for example, survive
* orientation changes.
*/
final Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
if (isPersistent()) {
// No need to save instance state since it's persistent
return superState;
}
// Save the instance state
final SavedState myState = new SavedState(superState);
myState.clickCounter = mClickCounter;
return myState;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (!state.
补充:移动开发 , Android ,