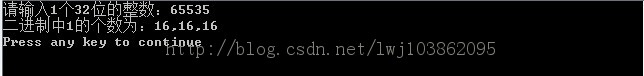
对于给定的词典,如下
[html]
一 ii i1
一一 ii i1 ii i1
一一一 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1
一一一一 ii i4 ii i1 ii i4 ii i1
一一一七 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 q i1
一一一三 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 s an1
一一一九 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 j iu3
一一一二 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 ee er4
一一一五 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 uu u3
一一一八 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 b a1
一一一六 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 l iu4
一一一四 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 s iy4
一一一零 ii i1 ii i1 ii i1 l ing2
一一七 ii i1 ii i1 q i1
此处略去很多个字
在语音识别时,训练和解码时都要用到词典,本文说明一个词典处理时的内存存储模型。
一,模型需求
模型包括如下信息
词典共有多少个词,这包括正常的词和特殊的词。
句子或文法的起始和结束用词。
停顿词,就是静音词,用于静音建模。
词的发音个数。可能有些词有多个发音,如“和”,就是一个常见的多音词。
建立语言模型时,是否依赖词。
二,模型实现
[cpp]
class Vocabulary
{
public:
int nWords ; // 总共多少个词
char **words ; // 所有词的数组,下标为词的序数,包括正常词和特殊词
int nNormWords ; // 正常词个数
int *normWordInds ; 正常词的序数
char specWordChar ; // 特殊词的标识,就是标识一个特殊词,如!一,表示一为特殊词
int nSpecWords ; // 特殊词的个数
int *specWordInds ; //所有特殊词的序数数组
int sentStartIndex ; // 句子或文法开始的词序号
int sentEndIndex ;// 句子或文法结束的词序号
int silIndex ;//静音词
bool fromBinFile ;
// 构造函数
Vocabulary() ;
Vocabulary(const char *lexFName , char specWordChar_='\0' ,
const char *sentStartWord=NULL , const char *sentEndWord=NULL ,
const char *silWord=NULL) ;
virtual ~DecVocabulary() ;
char *getWord( int index ) ; // 根据给定的序号,获取词,这个从词数组中获取。
int getNumPronuns( int index ) ; // 根据给定的序号,获取该词的发音个数,如果不是多音词,就返回1。
bool isSpecial( int index ) ; //序号对应的词是否是特殊词
bool getIgnoreLM( int index ); // 标记是否用于语言模型建模,一般都是依赖的,这个提高识别率。
int getIndex( const char *word , int guess=-1 ) ;//根据词获取序号,可以指定起始位置开始查找
private:
int nWordsAlloc ; // nWords记录词典包含多少个词,这个值记录共为内存词典大小。
bool *special ; // 指示词典中的词是否为特殊词
int *nPronuns ; // 每个词对应多少种不同的发音
/*** 添加一个词至内存词典中 ,并指示是否需要更新发音**/
int addWord( const char *word , bool registerPronun=true ) ;
};
三,构造函数过程
打开构造参数的词典文件,参数名lexFName,FILE *fd。
调用while( fgets(line,1000,fd)!=NULL )从fd中一行一行读取,然后分割取第一个域,并调用成员函数addWord往词典中加入词。
将开始和结束词加入词典中。
根据specWordChar来处理特殊词,就是判断第一个字节是否为specWordChar。统计特殊词和正常词的个数,并存入相应的内存中(见上文的类定义)。
四,加词实现
代码如下:
[cpp]
int Vocabulary::addWord( const char *word , bool registerPronun )
{
int cmpResult=0 , ind=-1 ;
//分配足够的空间存储
if ( nWords == nWordsAlloc ){
nWordsAlloc += 100 ;
words = (char **)realloc( words , nWordsAlloc*sizeof(char *) ) ;
nPronuns = (int *)realloc( nPronuns , nWordsAlloc*sizeof(int) ) ;
for ( int i=nWords ; i<nWordsAlloc ; i++ ){
words[i] = NULL ;
nPronuns[i] = 0 ;
}
}
if ( (word == NULL) || (word[0] == '\0') )
return -1 ;
if ( nWords > 0 )
cmpResult = strcasecmp( words[nWords-1] , word ) ;
//确保新词在适当的位置
if ( (cmpResult < 0) || (nWords == 0) ){
// The new word belongs at the end of the list
words[nWords] = new char[strlen(word)+1] ;
nPronuns[nWords] = 0 ;
strcpy( words[nWords] , word ) ;
ind = nWords ;
nWords++ ;
}else if ( cmpResult > 0 ){
for ( int i=0 ; i<nWords ; i++ ){
cmpResult = strcasecmp( words[i] , word ) ;
if ( cmpResult > 0 ){
nWords++ ;
for ( int j=(nWords-1) ; j>i ; j-- ){
words[j] = words[j-1] ;
nPronuns[j] = nPronuns[j-1] ;
}
words[i] = new char[strlen(word)+1] ;
strcpy( words[i] , word ) ;