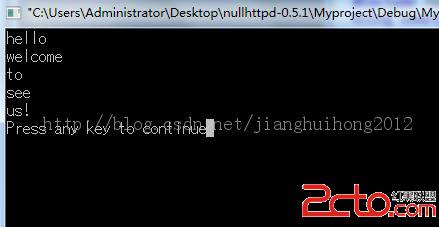
poj1009图像边缘检测
[cpp]
<span style="line-height: 1.1em; font-family: 'Lucida Grande', Verdana, 'Bitstream Vera Sans', Arial, sans-serif; ">从第一个点开始,依次算出与当前点的边缘差值相同的点的个数,如果某个重复次数大于 w * 5那么一定会有一连续的整行为0的输出。故此处可特判一下。然后在输出的过程中注意如果可以和前面的合并的就合并。判断的话主要判断某点正上方和正下方的点所能够达到最远的距离(即像素发生变化的地方)。超过了本行时变设为w;最后去3列的最小值。行数为当前点的行。具体见代码。</span>
描述
IONU Satellite Imaging, Inc. records and stores very large images using run length encoding. You are to write a program that reads a compressed image, finds the edges in the image, as described below, and outputs another compressed image of the detected edges.
A 易做图 edge detection algorithm sets an output pixel's value to be the maximum absolute value of the differences between it and all its surrounding pixels in the input image. Consider the input image below:

The upper left pixel in the output image is the maximum of the values |15-15|,|15-100|, and |15-100|, which is 85. The pixel in the 4th row, 2nd column is computed as the maximum of |175-100|, |175-100|, |175-100|, |175-175|, |175-25|, |175-175|,|175-175|, and |175-25|, which is 150.
Images contain 2 to 1,000,000,000 (109) pixels. All images are encoded using run length encoding (RLE). This is a sequence of pairs, containing pixel value (0-255) and run length (1-109). Input images have at most 1,000 of these pairs. Successive pairs have different pixel values. All lines in an image contain the same number of pixels.
输入
Input consists of information for one or more images. Each image starts with the width, in pixels, of each image line. This is followed by the RLE pairs, one pair per line. A line with 0 0 indicates the end of the data for that image. An image width of 0 indicates there are no more images to process. The first image in the example input encodes the 5x7 input image above.
输出
Output is a series of edge-detected images, in the same format as the input images, except that there may be more than 1,000 RLE pairs.
样例输入
7
15 4
100 15
25 2
175 2
25 5
175 2
25 5
0 0
10
35 500000000
200 500000000
0 0
3
255 1
10 1
255 2
10 1
255 2
10 1
255 1
0 0
0
样例输出
7
85 5
0 2
85 5
75 10
150 2
75 3
0 2
150 2
0 4
0 0
10
0 499999990
165 20
0 499999990
0 0
3
245 9
0 0
0
[cpp]
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include <memory.h>
# define min(a,b) (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)
int pix[1001], begin[1001], sum;
int ans[2012];
int cha[2012];
int cnt;
int w;
int *around;
int getPix (int nd) {
int p = 0, r = cnt + 1;
if (begin[r] <= nd) return r;
while (p + 1 < r) {
int mid = (p + r) >> 1;
if (begin[r] == nd) return r;
if (begin[mid] > nd) {
r = mid;
}
else if (begin[mid] < nd) {
p = mid;
}
else return mid;
}
return p;
}
int abs(int a) {
return a > 0 ? a : -a;
}
int getMax (int nd) {
int max = 0;
int l = 0, r = 8;
if (nd % w == 0) r = 5;
if (nd % w == 1) l = 3;
if (w == 1) {r = 5; l = 3;}
for (int i = l; i < r; ++ i) {
int t = nd + around[i];
if (t <= sum && t > 0) {
int m = pix[getPix(nd)];
int c = abs(pix[getPix(t)] - m);
max = max > c ? max : c;
}
}
return max;
}
int findEnd (int nd) {
int index = getPix (nd);
return begin[index + 1] - 1;
}
int getRow(int nd) {
return (nd - 1) / w + 1;
}
int getCol(int nd) {
return nd - (getRow(nd) - 1) * w;
}
int getPos (int row, int col) {
return w * (row - 1) + col;
}
int next (int nd) {
int a, b, c;
a = b = c = findEnd(nd);
if (nd - w > 0)
b = findEnd(nd - w);
if (nd + w <= sum)
c = findEnd(nd + w);
int row_a = getRow(a), col_a = getCol(a);
int row_b = getRow(b), col_b = getCol(b);
int row_c = getRow(c), col_c = getCol(c);
int row_nd = getRow(nd);// col_nd = getCol(nd);
if (a == b && b == c && nd - w > 0 && nd + w <= sum && row_c - 3 >= row_nd) return getPos(row_c - 2, w);
if (row_b >= row_nd) col_b = w;
if (row_c > row_nd + 1) col_c = w;
if (row_a > row_nd) col_a = w;
int col_min = min(col_a, min(col_b, col_c));
return getPos(row_nd, col_min);
}
int main () {
while ( (scanf("%d", &w), w) ) {
int a[] = {-1, -1 + w, -1 - w, w, -w, 1 + w, 1, 1 - w};
around = a;
int x, y;
cnt = -1;
sum = 0;
begin[0] = 1;
memset (cha, 0, sizeof(cha));
memset (ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
while ( (scanf ("%d %d", &x, &y), x + y ) ) {
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,