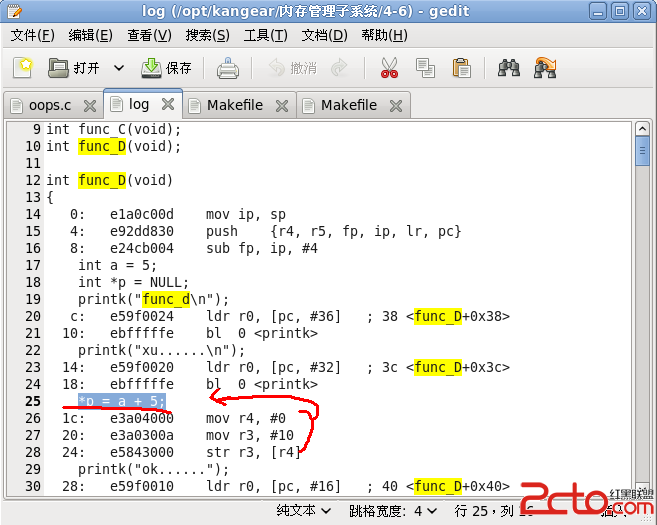
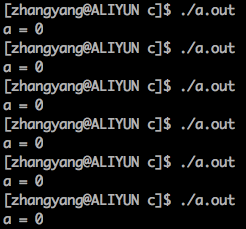
Fortran中主程序如何输入参数
Fortran中主程序如何输入参数?
主要使用下面的三个函数实现:
第一个:
COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT — Get number of command line arguments
Description:
COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT returns the number of arguments passed on the command line when the containing program was invoked.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Inquiry function
Syntax:
RESULT = COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT()
Arguments:
None
Return value:
The return value is an INTEGER of default kind.
Example:
program test_command_argument_count
integer :: count
count = command_argument_count()
print *, count
end program test_command_argument_count
COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT — Get number of command line arguments
Description:
COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT returns the number of arguments passed on the command line when the containing program was invoked.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Inquiry function
Syntax:
RESULT = COMMAND_ARGUMENT_COUNT()
Arguments:
None
Return value:
The return value is an INTEGER of default kind.
Example:
program test_command_argument_count
integer :: count
count = command_argument_count()
print *, count
end program test_command_argument_count
第二个:
GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT — Get command line arguments
Description:
Retrieve the NUMBER-th argument that was passed on the command line when the containing program was invoked.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Subroutine
Syntax:
CALL GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT(NUMBER [, VALUE, LENGTH, STATUS])
Arguments:
NUMBER Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind, NUMBER \geq 0
VALUE (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type CHARACTER and of default kind.
LENGTH (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind.
STATUS (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind.
Return value:
After GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT returns, the VALUE argument holds the NUMBER-th command line argument. If VALUE can not hold the argument, it is truncated to fit the length of VALUE. If there are less than NUMBER arguments specified at the command line, VALUE will be filled with blanks. If NUMBER = 0, VALUE is set to the name of the program (on systems that support this feature). The LENGTH argument contains the length of the NUMBER-th command line argument. If the argument retrieval fails, STATUS is a positive number; if VALUE contains a truncated command line argument, STATUS is -1; and otherwise the STATUS is zero.
Example:
PROGRAM test_get_command_argument
INTEGER :: i
CHARACTER(len=32) :: arg
i = 0
DO
CALL get_command_argument(i, arg)
IF (LEN_TRIM(arg) == 0) EXIT
WRITE (*,*) TRIM(arg)
i = i+1
END DO
END PROGRAM
GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT — Get command line arguments
Description:
Retrieve the NUMBER-th argument that was passed on the command line when the containing program was invoked.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Subroutine
Syntax:
CALL GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT(NUMBER [, VALUE, LENGTH, STATUS])
Arguments:
NUMBER Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind, NUMBER \geq 0
VALUE (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type CHARACTER and of default kind.
LENGTH (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind.
STATUS (Optional) Shall be a scalar of type INTEGER and of default kind.
Return value:
After GET_COMMAND_ARGUMENT returns, the VALUE argument holds the NUMBER-th command line argument. If VALUE can not hold the argument, it is truncated to fit the length of VALUE. If there are less than NUMBER arguments specified at the command line, VALUE will be filled with blanks. If NUMBER = 0, VALUE is set to the name of the program (on systems that support this feature). The LENGTH argument contains the length of the NUMBER-th command line argument. If the argument retrieval fails, STATUS is a positive number; if VALUE contains a truncated command line argument, STATUS is -1; and otherwise the STATUS is zero.
Example:
PROGRAM test_get_command_argument
INTEGER :: i
CHARACTER(len=32) :: arg
i = 0
DO
CALL get_command_argument(i, arg)
IF (LEN_TRIM(arg) == 0) EXIT
WRITE (*,*) TRIM(arg)
i = i+1
END DO
END PROGRAM
第三个:
GET_COMMAND — Get the entire command line
Description:
Retrieve the entire command line that was used to invoke the program.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Subroutine
Syntax:
CALL GET_COMMAND([COMMAND, LENGTH, STATUS])
Arguments:
COMMAND (Optional) shall be of type CHARACTER and of default kind.
LENGTH (Optional) Shall be of type INTEGER and of default kind.
STATUS (Optional) Shall be of type INTEGER and of default kind.
Return value:
If COMMAND is present, stores the entire command line that was used to invoke the program in COMMAND. If LENGTH is present, it is assigned the length of the command line. If STATUS is present, it is assigned 0 upon success of the command, -1 if COMMAND is too short to store the command line, or a positive value in case of an error.
Example:
PROGRAM test_get_command
CHARACTER(len=255) :: cmd
CALL get_command(cmd)
WRITE (*,*) TRIM(cmd)
END PROGRAM
GET_COMMAND — Get the entire command line
Description:
Retrieve the entire command line that was used to invoke the program.
Standard:
Fortran 2003 and later
Class:
Subroutine
Syntax:
CALL GET_COMMAND([COMMAND, LENGTH, STATUS])
Arguments:
COMMAND (Optional) shall be of type CHARACTER and of default kind.
LENGTH (Optional) Shall be of type INTEGER and of default kind.
STATUS (Optional) Shall be of type INTEGER and of default kind.
Return value:
If COMMAND is present, stores the entire command line that was used to invoke the program in COMMAND. If LENGTH is present, it is assigned the length of the command line. If STATUS is present, it is assigned 0 upon success of the command, -1 if COMMAND is too short to store the command line, or a positive value in case of an error.
Example:
PROGRAM test_get_command
CHARACTER(len=255) :: cmd
CALL get_command(cmd)
WRITE (*,*) TRIM(cmd)
END PROGRAM
补充:Web开发 , 其他 ,