Android RoboGuice使用指南(6):Instance Bindings
我们在前面例子Android RoboGuice 使用指南(4):Linked Bindings 时为简单起见,定义MyRectangle和MySquare时为它们定义了一个不带参数的构造函数,如MyRectangle的如下:
[java] public class MyRectangle extends Rectangle{
public MyRectangle(){
super(50,50,100,120);
}
public MyRectangle(int width, int height){
super(50,50,width,height);
}
}
public class MyRectangle extends Rectangle{
public MyRectangle(){
super(50,50,100,120);
}
public MyRectangle(int width, int height){
super(50,50,width,height);
}
}
实际上可以不需要这个不带参数的构造函数,可以使用Instance Bindings ,Instance Bindings可以将一个类型绑定到一个特定的实例对象,通常用于一个本身不依赖其它类的类型,如各种基本类型,比如:
[java] bind(String.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("JDBC URL"))
.toInstance("jdbc:mysql://localhost/pizza");
bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("login timeout seconds"))
.toInstance(10);
bind(String.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("JDBC URL"))
.toInstance("jdbc:mysql://localhost/pizza");
bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("login timeout seconds"))
.toInstance(10);
修改MyRectangle和MySquare的定义如下:
[java] public class MySquare extends MyRectangle {
@Inject
public MySquare(@Named("width") int width){
super(width,width);
}
}
...
public class MyRectangle extends Rectangle{
@Inject
public MyRectangle(@Named("width") int width,
@Named("height")int height){
super(50,50,width,height);
}
}
public class MySquare extends MyRectangle {
@Inject
public MySquare(@Named("width") int width){
super(width,width);
}
}
...
public class MyRectangle extends Rectangle{
@Inject
public MyRectangle(@Named("width") int width,
@Named("height")int height){
super(50,50,width,height);
}
}
去掉了无参数的构造函数,可以将标注为@Named(“width”)的int 类型绑定到100,添加下面绑定:
[java] bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("width"))
.toInstance(100);
bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("height"))
.toInstance(120);
bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("width"))
.toInstance(100);
bind(Integer.class)
.annotatedWith(Names.named("height"))
.toInstance(120);
运行这个例子,可以得到和前面例子同样的结果。此时使用Injector 构造一个MyRectangle 实例时,Injector自动选用带参数的那个构造函数,使用100,120为width和height注入参数,返回一个MyRectangle对象到需要引用的地方。
尽管可以使用Instance Bindings将一个类型映射到一个复杂类型的类实例,但RoboGuice不建议将Instance Bindings应用到复杂类型的实例,因为这样会使应用程序启动变慢。
正确的方法是使用@Provides 方法,将在下面介绍。
注:GuiceDemo 中的例子没用使用列表的方法来显示所有示例,如需运行所需示例,可以通过Run Configuration->设置Launch 的Activity:
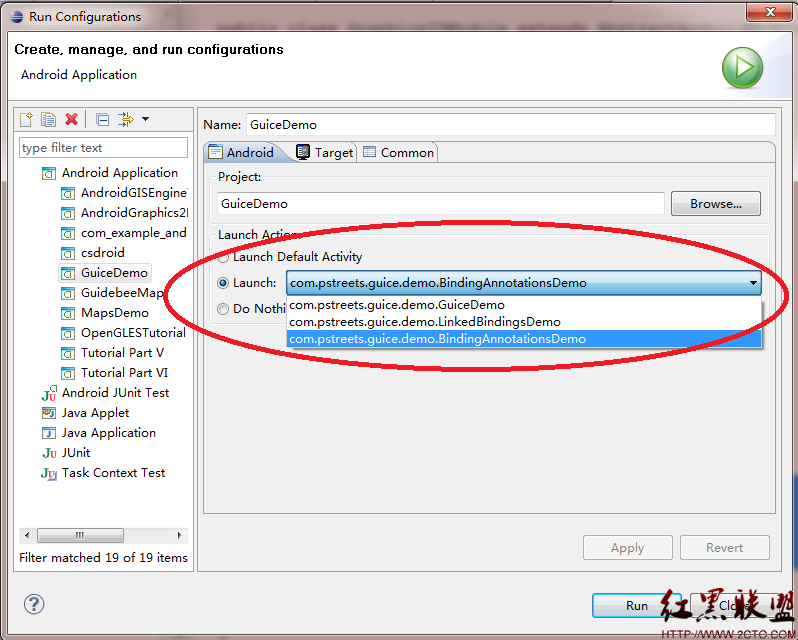
摘自 引路蜂移动软件
补充:移动开发 , Android ,