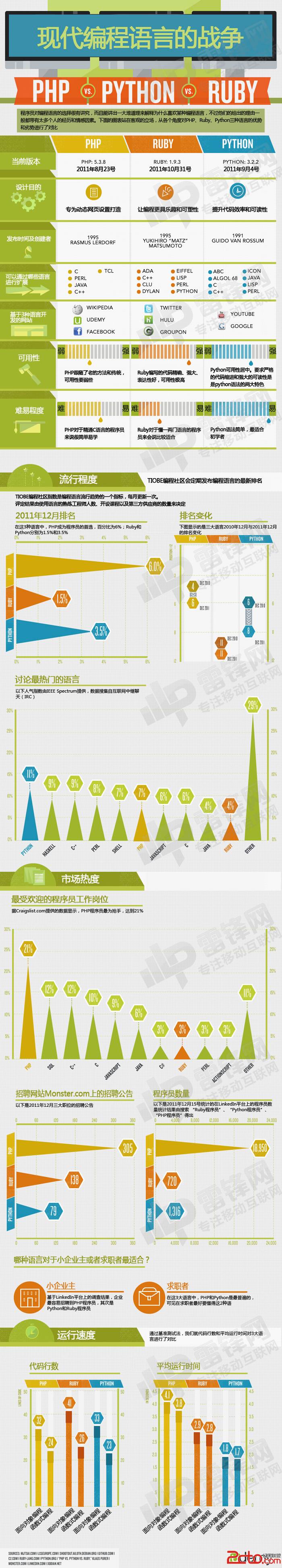
python入门
>>> 2+2 4 >>> # This is a comment ... 2+2 4 >>> 2+2 # and a comment on the same line as code 4 >>> (50-5*6)/4 5.0 >>> 8/5 # Fractions aren't lost when dividing integers 1.6
To do integer division and get an integer result, discarding any fractional result, there is another operator,//:
[python]
>>> # Integer division returns the floor:
... 7//3
2
>>> 7//-3
-3
>>> # Integer division returns the floor:
... 7//3
2
>>> 7//-3
-3
Complex numbers are also supported; imaginary numbers are written with a suffix ofj orJ. Complex numbers with a nonzero real component are written as(real+imagj), or can be created with thecomplex(real,imag) function.
[python]
>>> 1j * 1J
(-1+0j)
>>> 1j * complex(0, 1)
(-1+0j)
>>> 3+1j*3
(3+3j)
>>> (3+1j)*3
(9+3j)
>>> (1+2j)/(1+1j)
(1.5+0.5j)
>>> 1j * 1J
(-1+0j)
>>> 1j * complex(0, 1)
(-1+0j)
>>> 3+1j*3
(3+3j)
>>> (3+1j)*3
(9+3j)
>>> (1+2j)/(1+1j)
(1.5+0.5j)
To extract these parts from a complex number z, usez.real andz.imag.
[python]
>>> a=1.5+0.5j
>>> a.real
1.5
>>> a.imag
0.5
>>> a=1.5+0.5j
>>> a.real
1.5
>>> a.imag
0.5
the last printed expression is assigned to the variable _
[python]
>>> tax = 12.5 / 100
>>> price = 100.50
>>> price * tax
12.5625
>>> price + _
113.0625
>>> round(_, 2)
113.06
>>> tax = 12.5 / 100
>>> price = 100.50
>>> price * tax
12.5625
>>> price + _
113.0625
>>> round(_, 2)
113.06
2:Strings
[python]
>> 'spam eggs'
'spam eggs'
>>> 'doesn\'t'
"doesn't"
>>> "doesn't"
"doesn't"
>>> '"Yes," he said.'
'"Yes," he said.'
>>> "\"Yes,\" he said."
'"Yes," he said.'
>>> '"Isn\'t," she said.'
'"Isn\'t," she said.'
>>> 'spam eggs'
'spam eggs'
>>> 'doesn\'t'
"doesn't"
>>> "doesn't"
"doesn't"
>>> '"Yes," he said.'
'"Yes," he said.'
>>> "\"Yes,\" he said."
'"Yes," he said.'
>>> '"Isn\'t," she said.'
'"Isn\'t," she said.'
Continuation lines can be used, with a backslash as the last character on the line indicating that the next line is a logical continuation of the line:
[python]
>>> hello="this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd"
>>> print(hello);
>>> hello="this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd"
>>> print(hello);[python] view plaincopyprint?this is not
asdfasdf
aksdfasd
this is not
asdfasdf
aksdfasd
a “raw” string:
[python]
>>> hello=r"this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd"
>>> print(hello);
>>> hello=r"this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd"
>>> print(hello);[python] view plaincopyprint?this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd
this is not \n\
asdfasdf\n\
aksdfasd
Strings can be concatenated (glued together) with the + operator, and repeated with *:
[python]
>>> hello='Hello';
>>> world='World';
>>> hello=hello+world;
>>> hello
'HelloWorld'
>>> hello='Hello';
>>> world='World';
>>> hello=hello+world;
>>> hello
'HelloWorld'[python] view plaincopyprint?>>> '<'+hello*5+'>'
'<HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld>'
>>> '<'+hello*5+'>'
'<HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld>'
补充:Web开发 , Python ,