android应用开发全程实录-实现甩动拨打和挂断电话
今天继续给大家带来《Android应用开发全程实录》中的章节,这部分是讲传感器中的一个实例。
通过上面的例子我们学会了如何获得某种类型的传感器,下面通过一个实例来学习如何使用某一个类型的传感器。我们以加速传感器为例,来实现这样一个功能:摇动手机便自动拨打某亲情号码,并实现再次摇动则挂机的功能。
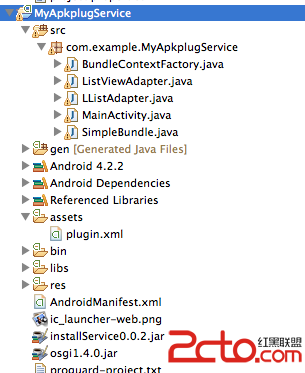
工程目录:EX_12_03
第一步,UI布局main.xml的代码如下,其运行效果如图12-10所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="当前状态:就绪"
android:id="@+id/state"
android:textColor="#ff0000" />
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/call"
android:text="打电话(10086)"/>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/stop"
android:text="挂机"/>
</LinearLayout>
第二步,挂电话需要用到系统的Itelephony类的支持,由于Google从Android 2.1 SDK版本后,屏蔽了com.android.internal.telephony. Itelephony类,因此,需要从Android源码下载,找到该类并导入到工程目录下,记得包名一致。
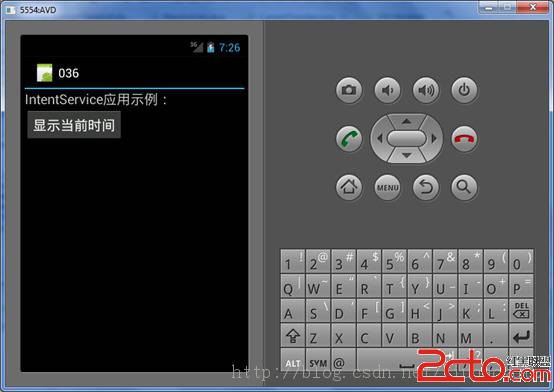
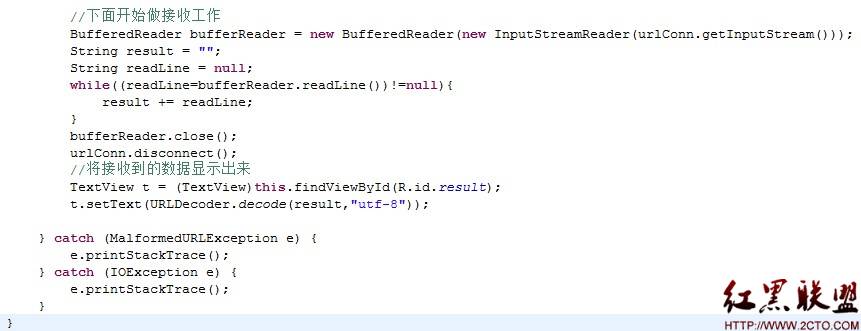
第三步,Activity类ShakeSensorActivity的实现。该类实现SensorListener接口,添加加速度侦听事件,通过判断设备X、Y、Z方向的总晃动值来判断是否启动打电话和挂机操作。以拨打10086测试为例,当设备总晃动值大于100作为一个测试判断点,如果当前没有在通话界面,就通过Intent启动拨打电话,否则就挂机操作。设备摇动时,启动电话、挂机的界面状态如图图12-11、图12-12所示。

▲图12-10 软件运行效果图

▲图12-11 电话启动界面
 图12-12 摇动设备挂机时的状态界面
图12-12 摇动设备挂机时的状态界面
下面就来看看代码:
public class ShakeSensorActivity extends Activity implements SensorListener { private float lastX; private float lastY; private float lastZ; private View mainView; private long currTime; private long lastTime; private long duration;// 持续时间
private float currShake; private float totalShake; private ITelephony iTelephony; private boolean isCalling = false; SensorManager sm = null; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); mainView = LinearLayout.inflate(this, R.layout.main, null); setContentView(mainView); ((Button) mainView.findViewById(R.id.call)).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 打电话 callPhoneNumber10086(); } }); ((Button) mainView.findViewById(R.id.stop)).setOnClickListener(new OnClick- Listener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 挂机 closePhone(); } }); // 获取传感器管理器 sm = (SensorManager) getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE); // 注册加速度传感器 sm.registerListener(this, SensorManager.SENSOR_ACCELEROMETER,SensorManager. SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL); } @Override public void finish() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.finish(); sm.unregisterListener(this);// 注销侦听 } @Override public void onAccuracyChanged(int sensor, int accuracy) { // 精度改变,该方法实质上不做任何操作,它只在每次调用时,添加一个日志项 } @Override public void onSensorChanged(int sensor, float[] values) { float x = values[0]; float y = values[1]; float z = values[2]; currTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (lastX == 0 && lastY == 0 && lastZ == 0) { // 第一次shake lastTime = currTime; } if (currTime - lastTime > 200)
{// 200毫秒检测一次 duration = currTime - lastTime; currShake = (Math.abs(x - lastX) + Math.abs(y - lastY) + Math.abs(z - lastZ))/ duration * 200; } totalShake = totalShake + currShake; if (totalShake > 100) { totalShake = 0;// 重置为0,重新累计计数
lastX = 0; lastY = 0; lastZ = 0; lastTime = 0; currTime = 0; if (!isCalling) { callPhoneNumber10086(); ((TextView) mainView.findViewById(R.id.state)).setText("当前状态: 通话中..."); } else { closePhone(); ((TextView) mainView.findViewById(R.id.state)).setText("当前状态:通话结束..."); } } lastX = x; lastY = y; lastZ = z; lastTime = currTime; } /** * tell 10086打开通话界面 */ private synchronized void callPhoneNumber10086() { isCalling = true; Intent myIntentDial = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL,Uri.parse("tel:" + 10086)); startActivity(myIntentDial); } /** * 结束通话 */ private synchronized void closePhone() { try { getTelephony(); iTelephony.endCall(); isCalling = false; } catch (RemoteException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 初始电话 实例 */
public void getTelephony() { TelephonyManager telMgr = (TelephonyManager) this.getSystemService(Service. TELEPHONY_SERVICE); Class<TelephonyManager> c = TelephonyManager.class; Method getITelephonyMethod = null; try { getITelephonyMethod = c.getDeclaredMethod("getITelephony",(Class[]) null); getITelephonyMethod.setAccessible(true); } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { iTelephony = (ITelephony) getITelephonyMethod.invoke(telMgr,(Object[])null); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
www.zzzyk.com
通过getTelephony()方法,初始一个iTelephony实例,方便调用,目前只用到了挂机关闭通话,打电话也可以通过iTelephony.dial(“10086”)直接拨打。这样就轻松实现了甩动打挂电话功能了
摘自 notice501的专栏
补充:移动开发 , Android ,