Android ApiDemos示例解析(180):Views->Lists->13. Slow Adapter
对于一个长列表,如果每个列表项载入比较费时( 比如从网络下载图像),如果此时需要快速滚动列表,可以先给列表项使用一个替代名称或是其它可以快速载入的项,当列表停止滚动时再载入实际的列表项,这样可以大大提高列表的响应性能。
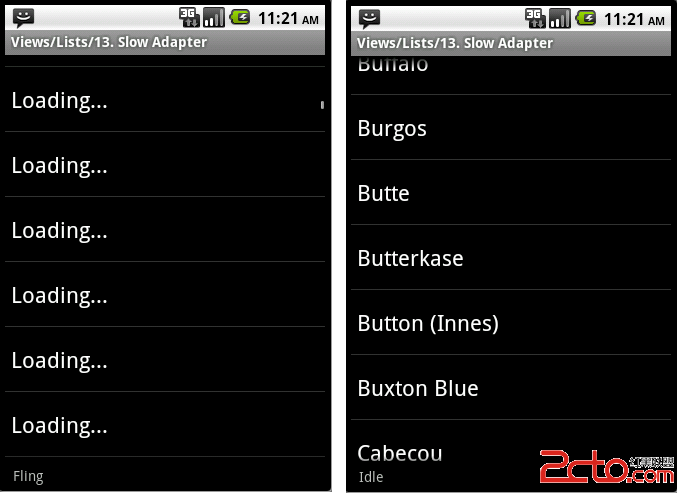
本例在ListView中显示一个字符串数组来模拟一个费时的列表项载入(尽管显示文字列表项实际上很快),当列表开始滚动或是快速飞行时,使用一个临时数据来绑定列表项(如Loading …),而在列表停止滚动时,使用实际需要显示的文字替换之前显示的临时数据。
看看自定义SlowAdapter的getView 的实现:
[java]
public View getView(int position,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextView text;
if (convertView == null) {
text = (TextView)mInflater.inflate
(android.R.layout.易做图_list_item_1,
parent, false);
} else {
text = (TextView)convertView;
}
if (!mBusy) {
text.setText(mStrings[position]);
// Null tag means the view has the c
//orrect data
text.setTag(null);
} else {
text.setText("Loading...");
// Non-null tag means the view still
//needs to load it's data
text.setTag(this);
}
return text;
}
public View getView(int position,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextView text;
if (convertView == null) {
text = (TextView)mInflater.inflate
(android.R.layout.易做图_list_item_1,
parent, false);
} else {
text = (TextView)convertView;
}
if (!mBusy) {
text.setText(mStrings[position]);
// Null tag means the view has the c
//orrect data
text.setTag(null);
} else {
text.setText("Loading...");
// Non-null tag means the view still
//needs to load it's data
text.setTag(this);
}
return text;
}
可以看到在ListView busy(滚动时) ,将textview 的文字设置成临时数据(loading …”) ,并把textView 的tag 设为非空, TextView 的Tag 可以使用任何对象,本例用它来做个标记,非空时表示当前TextView使用的是临时数据。 而的ListView不忙时(停止滚动),将TextView设置成实际需要显示的文字(或是其它费时的操作),并把它的Tag设为空,表示TextView显示的是真实数据。
为ListView 添加滚动事件处理
[java]
getListView().setOnScrollListener(this);}
...
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view,
int scrollState) {
switch (scrollState) {
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE:
mBusy = false;
int first = view.getFirstVisiblePosition();
int count = view.getChildCount();
for (int i=0; i<count; i++) {
TextView t = (TextView)view.getChildAt(i);
if (t.getTag() != null) {
t.setText(mStrings[first + i]);
t.setTag(null);
}
}
mStatus.setText("Idle");
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL:
mBusy = true;
mStatus.setText("Touch scroll");
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING:
mBusy = true;
mStatus.setText("Fling");
break;
}
}
getListView().setOnScrollListener(this);}
...
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view,
int scrollState) {
switch (scrollState) {
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE:
mBusy = false;
int first = view.getFirstVisiblePosition();
int count = view.getChildCount();
for (int i=0; i<count; i++) {
TextView t = (TextView)view.getChildAt(i);
if (t.getTag() != null) {
t.setText(mStrings[first + i]);
t.setTag(null);
}
}
mStatus.setText("Idle");
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL:
mBusy = true;
mStatus.setText("Touch scroll");
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING:
mBusy = true;
mStatus.setText("Fling");
break;
}
}
在ListView 滚动或是飞速滑动时,将busy设为true, 当滚动停止时SCROLL_STATE_IDLE ,busy为false, 并根据TextView的Tag值判断是否需要显示实际的文字串。
本例最下面并使用了一个文本框显示了当前ListView的滚动状态。
补充:移动开发 , Android ,