java设计模式——装饰模式(Decorator)
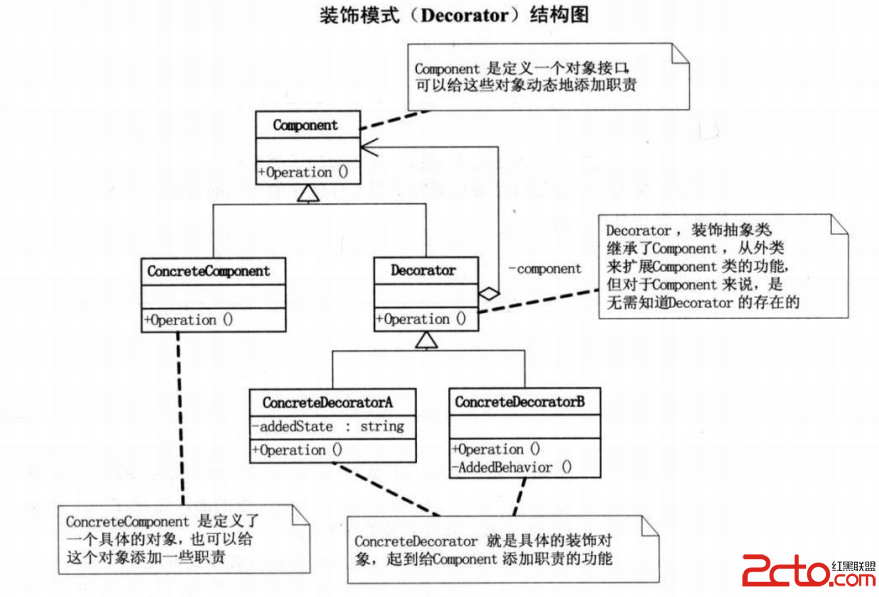
装饰模式(Decorator),动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更为灵活。装饰模式适应场合:装饰模式是为已有功能动态地添加更多功能的一种方式当系统需要新功能的时候,是向旧的类中添加新的代码。这些新加的代码通常装饰了原有类的核心职责或主要行为在主类中加入了新的字段,新的方法和新的逻辑,从而增加了主类的复杂度,而这些新加入的东西仅仅是为了满足一些只在某种特定情况下才会执行的特殊行为的需要。装饰模式把每个要装饰的功能放在单独的类中,并让这个类包装它所要装饰的对象,因此,当需要执行特殊行为时,客户代码就可以再运行时根据需要有选择地,安顺序地使用装饰功能包装对象了装饰模式的有点是把类中的装饰功能从类中搬移去除,这样可以简化原有的类,更能有效地把类的核心职责和装饰功能区分开,而且可以去除相关类中重复的装饰逻辑Component是定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责。ConcreteComponent是定义了一个具体的对象,也可以给这个对象添加一些职责,Decorator,装饰抽象类,继承了Component从外类来扩展Component类的功能,但对于Component来说,是无需知道Decorator的存在的,至于ConcreteDecorator就具体的装饰对象,起到给Component添加职责的功能。public interface Component {public void Operation();}public class Decorator implements Component{protected Component component;public void setComponent(Component component) {this.component = component;}@Overridepublic void Operation() {if(component!=null){component.Operation();}}}public class ConcreteComponent implements Component{@Overridepublic void Operation() {System.out.println("具体对象的操作");}}public class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator{private String addedState;@Overridepublic void Operation(){super.Operation();addedState = "New State";System.out.println("具体装饰对象A的操作");}}public class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator{private String addedState;@Overridepublic void Operation(){super.Operation();AddedBehavior();System.out.println("具体装饰对象B的操作");}private void AddedBehavior(){}}public class DetoratorMain {public static void main(String[] args) {ConcreteComponent c = new ConcreteComponent();ConcreteDecoratorA d1 = new ConcreteDecoratorA();ConcreteDecoratorB d2 = new ConcreteDecoratorB();d1.setComponent(c);d2.setComponent(d1);d2.Operation();}}Demo:public class Person {public Person(){};private String name;public Person(String name){this.name=name;}public void show(){System.out.println("装扮的"+name);}}public class Finery extends Person{protected Person component;public void Decorate(Person component){this.component = component;}@Overridepublic void show(){if(component!=null){component.show();}}}public class BigTrouser extends Finery{@Overridepublic void show(){System.out.println("垮裤");super.show();}}public class Sneakers extends Finery{@Overridepublic void show(){System.out.println("破球鞋");super.show();}}public class TShirts extends Finery{@Overridepublic void show(){System.out.println("大T恤");super.show();}}public class DecoratorMain {public static void main(String[] args){Person daixu = new Person("待续");System.out.println("第一种装饰");Sneakers pqx = new Sneakers();BigTrouser kk = new BigTrouser();TShirts dtx = new TShirts();补充:软件开发 , Java ,上一个:java函数
下一个:Java--调试--单步调试,断言,单元测试
- 更多JAVA疑问解答:
- java怎么在线读取ftp服务器上的文件内容
- 关于程序员的职业规划
- HTML和JSP矛盾吗?
- java小程序如何打包?
- java怎么split路径文件名?
- 关于Hibernate实体自身多对一的抓取问题
- 关于apache2+tomcat群集出现的问题
- SSH 导入导出excel 谁有这块的资料吗?
- springmvc 加载一个jsp页面执行多个方法 报404
- 关于用jquery 导入 excel
- java对时间进行循环放到List中
- 一个图片的输入输出程序,第一次调用某方法会中断,第二次调用则正常
- 请上过传智播客的人说一下传智播客怎么样呀!是不是像它说的那样好呀!
- spring的schema怎么配置
- 【菜鸟求助】SSH中怎么从JSP页面往后台传值呢