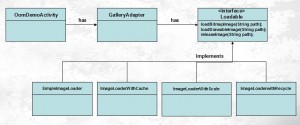
Android四大天王之Service
本节我们学习Android四大天王的Service,如果把Activity比作是前台程序,那么Service就是后台程序,Service的整个生命周期只会在后台执行。它一般没有用户操作界面,运行于系统中不容易被用户发觉,可以用来开发如监控之类的程序。与Activity一样,Service也是通过Intent来调用。
一、创建Service
1.继承API的Service类[java]
public class CustomService extends Service {...}
public class CustomService extends Service {...}2.在AndroidManifest.xml的<application>标签中对创建的Service进行注册
[html]
<service android:name=".MyService" />
<service android:name=".MyService" />二、启动Service
服务不能自己运行,需要通过调用Context.startService()或Context.bindService()方法启动服务。这两个方法使用场合有所不同。
1.采用Context.startService()方法启动服务
当服务未被创建时,系统会先调用服务的onCreate()方法,接着调用onStartCommand(...)方法。如果调用startService()方法前服务已经被创建,多次调用startService()方法并不会导致多次创建服务,但会导致多次调用onStartCommand(...)方法。采用startService()方法启动的服务,只能调用stopService()方法结束服务,服务结束时会调用onDestroy()方法。采用这种方式启用服务,调用者与服务之间没有关联,即使调用者退出了,服务仍然运行。
2.采用Context.bindService()方法启动服务
当服务未被创建时,系统会先调用服务的onCreate()方法,接着调用onBind()方法。这个时候调用者和服务绑定在一起,调用者退出了,系统就会先调用服务的onUnbind()方法,接着调用onDestroy()方法。如果调用bindService()方法前服务已经被绑定,多次调用bindService()方法并不会导致多次创建服务及绑定(也就是说onCreate()和onBind()方法并不会被多次调用)。如果调用者希望与正在绑定的服务解除绑定,可以调用unbindService()方法,调用该方法也会导致系统调用服务的onUnbind()方法,接着调用onDestroy()方法。采用这种方式启用服务,调用者与服务绑定在了一起,调用者一旦退出,服务也就终止。
三、Service生命周期
既然官方没有为Service生命周期提供示意图,那么我们就模仿Activity生命周期示意图绘制一张,然后再进行总结。
从上图可以看出,其实Service的生命周期可以分为如下两个场景:
1.由Context.startService()启动生命周期:startService() ☞ onCreate() ☞ onStartCommand() ☞ stopService() ☞ onDestroy()
多次调用startService()方法尽管不会多次创建服务,但onStartCommand()方易做图被多次调用。
2.由Context.bindService()启动生命周期:bindService() ☞ onCreate() ☞ onBind() ☞ unbindService() ☞ onUnbind() ☞ onDestroy()
当调用者与服务已经绑定时,多次调用bindService()方法并不会导致onBind()方法被多次调用。
四、Service案例
1.案例代码陈列
AndroidManifest.xml
[html]
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="cn.lynn.service"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="15" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" />
</application>
</manifest>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="cn.lynn.service"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="15" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" />
</application>
</manifest>strings.xml
[html]
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Android四大天王之Service</string>
</resources>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Android四大天王之Service</string>
</resources>main.xml[html] view plaincopyprint?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStartMyService"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
补充:移动开发 , Android ,