自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
18.4 完整解决方案
为了能够解释机器人控制指令,Sunny软件公司开发人员使用解释器模式来设计和实现机器人控制程序。针对五条文法规则,分别提供五个类来实现,其中终结符表达式direction、action和distance对应DirectionNode类、ActionNode类和DistanceNode类,非终结符表达式expression和composite对应SentenceNode类和AndNode类。
我们可以通过抽象语法树来表示具体解释过程,例如机器人控制指令“downrun 10 and left move20”对应的抽象语法树如图18-4所示:
、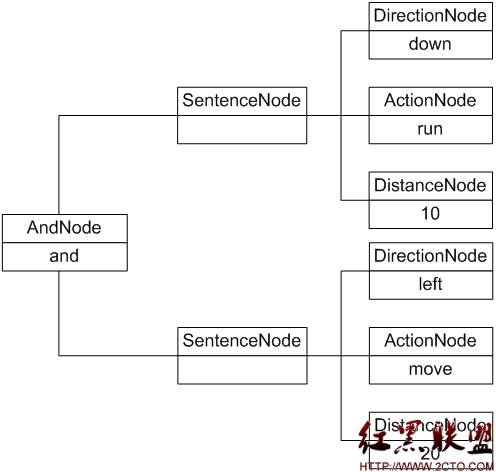
图18-4 机器人控制程序抽象语法树实例
机器人控制程序实例基本结构如图18-5所示:

图18-5 机器人控制程序结构图
在图18-5中,AbstractNode充当抽象表达式角色,DirectionNode、ActionNode和DistanceNode充当终结符表达式角色,AndNode和SentenceNode充当非终结符表达式角色。完整代码如下所示:
[java] view plaincopy
//注:本实例对机器人控制指令的输出结果进行模拟,将英文指令翻译为中文指令,实际情况是调用不同的控制程序进行机器人的控制,包括对移动方向、方式和距离的控制等
import java.util.*;
//抽象表达式
abstract class AbstractNode {
public abstract String interpret();
}
//And解释:非终结符表达式
class AndNode extends AbstractNode {
private AbstractNode left; //And的左表达式
private AbstractNode right; //And的右表达式
public AndNode(AbstractNode left, AbstractNode right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
//And表达式解释操作
public String interpret() {
return left.interpret() + "再" + right.interpret();
}
}
//简单句子解释:非终结符表达式
class SentenceNode extends AbstractNode {
private AbstractNode direction;
private AbstractNode action;
private AbstractNode distance;
public SentenceNode(AbstractNode direction,AbstractNode action,AbstractNode distance) {
this.direction = direction;
this.action = action;
this.distance = distance;
}
//简单句子的解释操作
public String interpret() {
return direction.interpret() + action.interpret() + distance.interpret();
}
}
//方向解释:终结符表达式
class DirectionNode extends AbstractNode {
private String direction;
public DirectionNode(String direction) {
this.direction = direction;
}
//方向表达式的解释操作
public String interpret() {
if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("up")) {
return "向上";
}
else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("down")) {
return "向下";
}
else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("left")) {
return "向左";
}
else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("right")) {
return "向右";
}
else {
return "无效指令";
}
}
}
//动作解释:终结符表达式
class ActionNode extends AbstractNode {
private String action;
public ActionNode(String action) {
this.action = action;
}
//动作(移动方式)表达式的解释操作
public String interpret() {
if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("move")) {
return "移动";
}
else if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("run")) {
return "快速移动";
}
else {
return "无效指令";
}
}
}
//距离解释:终结符表达式
class DistanceNode extends AbstractNode {
private String distance;
public DistanceNode(String distance) {
this.distance = distance;
}
//距离表达式的解释操作
public String interpret() {
return this.distance;
}
}
//指令处理类:工具类
class InstructionHandler {
private String instruction;
private AbstractNode node;
public void handle(String instruction) {
AbstractNode left = null, right = null;
AbstractNode direction = null, action = null, distance = null;
Stack stack = new Stack(); //声明一个栈对象用于存储抽象语法树
String[] words = instruction.split(" "); //以空格分隔指令字符串
&nb
补充:软件开发 , Java ,