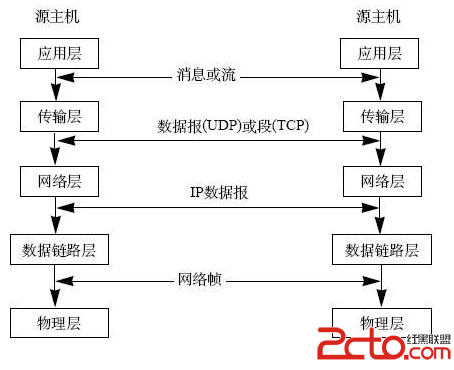
(一)自定义View类
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class CrossView extends View {
private float mRotation;
private Paint mPaint;
public CrossView( Context context, AttributeSet attrs ) {//AttributeSet对象在实例化时被系统传给了视图
super( context, attrs );
//start 创建paint对象
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias( true );
mPaint.setColor( 0xFFFFFFFF );
//end 创建paint对象
//使用obtainStyledAttributes方法来创建一个TypedArray,这是访问存储于AttributeSet中的值的一个方便类,这类执行内部缓存,
//所以当你结束使用它之后随时调用回收函数。注意:需同时使用<declare-styleable>名称和<arr>名称的访问自定义属性
TypedArray arr = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes( attrs,R.styleable.cross );
int color = arr.getColor( R.styleable.cross_android_color, Color.WHITE );
float rotation = arr.getFloat( R.styleable.cross_rotation, 0f );
//remember to call this when finished
arr.recycle();
setColor(color);
setRotation(rotation);
}
private void setRotation( float rotation ) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mRotation = rotation;
}
private void setColor( int color ) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mPaint.setColor( color );
}
//重写onMeasure方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure( int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec ) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onMeasure( widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec );
//需要使用计算好的宽和高的值作为该方法的实参
setMeasuredDimension( calculateMeasure(widthMeasureSpec), calculateMeasure(heightMeasureSpec) );
}
float[] mPoints = {0.5f,0f,0.5f,1f,0f,0.5f,1f,0.5f};
@Override
protected void onDraw( Canvas canvas ) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw( canvas );
canvas.save();//所有的在画布上绘图的调用都应当受对应的sava()和restore()的约束
int scale = getWidth();
canvas.scale( scale, scale );
canvas.rotate( mRotation );
canvas.drawLines( mPoints, mPaint );//绘制十字的两条线
canvas.restore();//所有的在画布上绘图的调用都应当受对应的sava()和restore()的约束
}
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 100;//默认的试图尺寸
//实现计算测量值的代码
private int calculateMeasure(int measureSpec){
int result = ( int ) ( DEFAULT_SIZE*getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density );
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode( measureSpec );//在MeasureSpec中检索模式
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize( measureSpec );//在MeasureSpec中检索尺寸
//基于模式选择尺寸
if(specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
result = specSize;
}else if(specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
result = Math.min( result, specSize );
}
return result;
}
}
(二)自定义属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 该文件被放置在res/values/目录下 -->
<resources>
<!-- 声明属性 -->
<declare-styleable name="cross">
<attr name="android:color"/>
<attr name="rotation" format="string"/>
</declare-styleable>
<!--
<attr name="test" format="string"/>
<declare-styleable name="foo">
<attr name="test"/>
</declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="bar">
<attr name="test"/>
</declare-styleable> -->
</resources>
(三)在XML中使用自定义View
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 要使用在XML中的自定义属性,首先必须为视图声明命名空间 -->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:example="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<!-- 添加CrossView -->
<com.example.CrossView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<com.example.CrossView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
example.rotation="30"
android:color="#0000FF"/>
/>
<com.example.CrossView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
example.rotation="40"
android:color="#FFFF00"
/>
</LinearLayout>