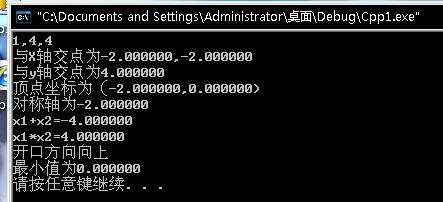
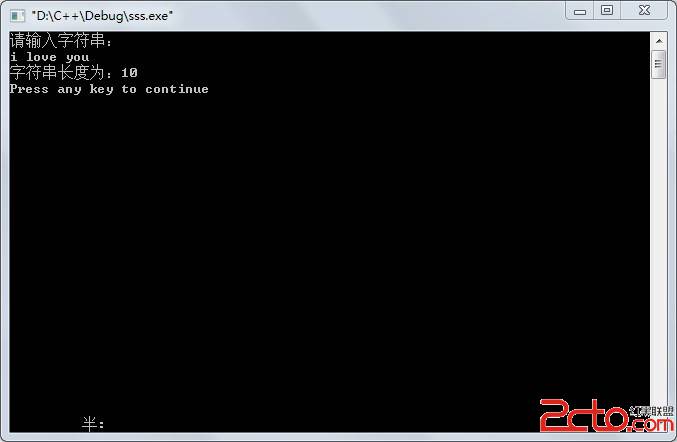
openRtsp分析
在SingleStep中看到检测到select中write准备就绪。即跳到connectionHandler[cpp]
void RTSPClient::connectionHandler(void* instance, int /*mask*/) {
RTSPClient* client = (RTSPClient*)instance;
client->connectionHandler1();
}
[cpp]
void RTSPClient::connectionHandler1() {
// Restore normal handling on our sockets:
envir().taskScheduler().disableBackgroundHandling(fOutputSocketNum);
envir().taskScheduler().setBackgroundHandling(fInputSocketNum, SOCKET_READABLE,
(TaskScheduler::BackgroundHandlerProc*)&incomingDataHandler, this);
// Move all requests awaiting connection into a new, temporary queue, to clear "fRequestsAwaitingConnection"
// (so that "sendRequest()" doesn't get confused by "fRequestsAwaitingConnection" being nonempty, and enqueue them all over again).
RequestQueue tmpRequestQueue(fRequestsAwaitingConnection);
RequestRecord* request;
// Find out whether the connection succeeded or failed:
do {
int err = 0;
SOCKLEN_T len = sizeof err;
if (getsockopt(fInputSocketNum, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, (char*)&err, &len) < 0 || err != 0) {
envir().setResultErrMsg("Connection to server failed: ", err);
if (fVerbosityLevel >= 1) envir() << "..." << envir().getResultMsg() << "\n";
break;
}
// The connection succeeded. If the connection came about from an attempt to set up RTSP-over-HTTP, finish this now:
if (fVerbosityLevel >= 1) envir() << "...remote connection opened\n";
if (fHTTPTunnelingConnectionIsPending && !setupHTTPTunneling2()) break;
// Resume sending all pending requests:
while ((request = tmpRequestQueue.dequeue()) != NULL) {
sendRequest(request);
}
return;
} while (0);
// An error occurred. Tell all pending requests about the error:
resetTCPSockets(); // do this now, in case an error handler deletes "this"
while ((request = tmpRequestQueue.dequeue()) != NULL) {
handleRequestError(request);
delete request;
}
}
上面的代码中先清除掉connect Handing然后添加上read set ,检测到connect执行成功,将上次fRequestsAwaitingConnection出列,如果有未执行的request会重新执行sendRequest执行。在上次执行sendRequest的时候那个request是option的发送请求。这里就先再次进入sendRequest先通过commandName判断要发送什么命令。option中可以看到什么都没执行然后就是发送命令的拼接。然后就执行send将cmd发送出去。至此发送option的全部动作已经完成,下面我们再来看option命令respone的接收。
在connectionHandler1()中我们看到把fInputSocketNum加入到了SOCKET_READABLE集中,回调函数是incomingDataHandler。同样SingleStep 中select有read的时候会调用这个回调函数。现在来看看
[cpp]
void RTSPClient::incomingDataHandler(void* instance, int /*mask*/) {
RTSPClient* client = (RTSPClient*)instance;
client->incomingDataHandler1();
}
[cpp]
void RTSPClient::incomingDataHandler1() {
struct sockaddr_in dummy; // 'from' address - not used
int bytesRead = readSocket(envir(), fInputSocketNum, (unsigned char*)&fResponseBuffer[fResponseBytesAlreadySeen], fResponseBufferBytesLeft, dummy);
handleResponseBytes(bytesRead);
}
readsocket没什么可看的,就是执行recvfrom接收字节到fResponseBuffer中。然后执行的就是handleResponseBytes,可以看到handleResponseBytes中的内容很多,主要是对response的分析。主要看到最后有这句代码:
[cpp]
if (foundRequest != NULL && foundRequest->handler() != NULL) {
int resultCode;
char* resultString;
if (responseSuccess) {
if (responseCode == 200) {
resultCode = 0;
resultString = numBodyBytes > 0 ? strDup(bodyStart) : strDup(publicParamsStr);
// Note: The "strDup(bodyStart)" call assumes that the body is encoded without interior '\0' bytes
} else {
resultCode = responseCode;
resultString = strDup(responseStr);
envir().setResultMsg(responseStr);
}
(*foundRequest->handler())(this, resultCode, resultString);
} else {
// An error occurred parsing the response, so call the handler, indicating an error:
handleRequestError(foundRequest);
}
}
这里面的(*foundRequest->handler())(this, resultCode, resultString);就是执行 getOptions(continueAfterOPTIONS);中的continueAfterOPTIONS。
通过对option命令的发送和接收可以看到其他的命令的发送和接收是差不多的流程,详细过程就不一一列出。
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,