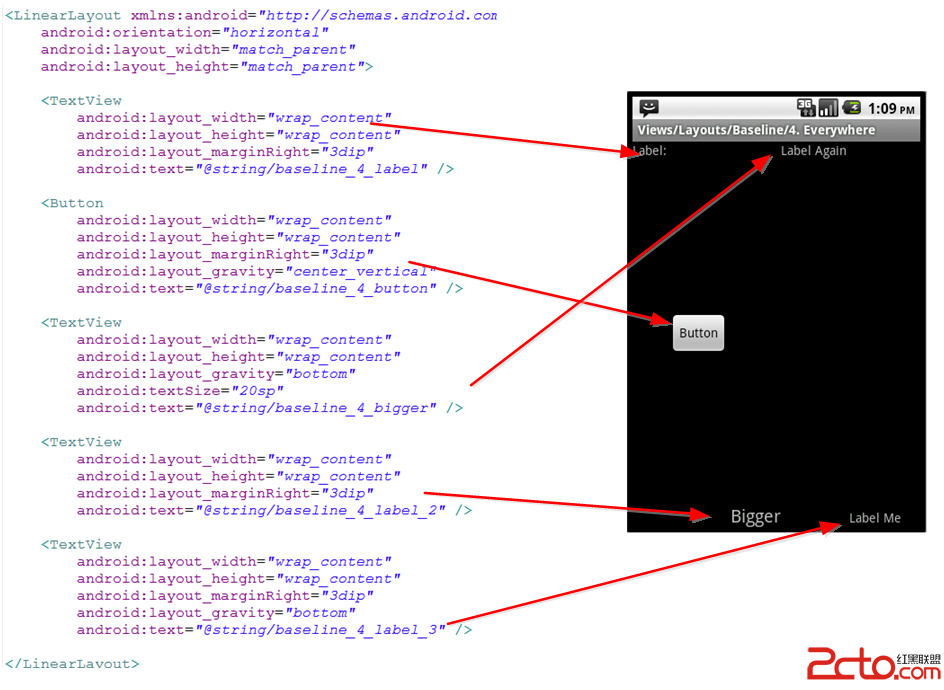
Android利用setLayoutParams在代码中调整布局(Margin和居中)
MainActivity如下:
package cn.testfixmargin;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.app.Activity;
/**
* Demo描述:
* 在代码中设置布局的属性
* 比如Margin和居中
*
* 注意事项:
* 参见代码中的详细注释
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView mTextView;
private Button mButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
init();
}
private void init(){
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(displayMetrics);
float density=displayMetrics.density;
float fontScale = displayMetrics.scaledDensity;
System.out.println("density="+density+",fontScale="+fontScale);
mTextView=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
mButton=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
}
private class OnClickListenerImpl implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// //--------以下为测试1 在代码中为控件设置Margin--------
// //注意:
// //1 此处的new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h)参数w,h指的是
// // 该控件的父控件的在布局文件中所设置的宽和高
// //2 此处必须使用RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT()
// // 因为其父类为RelativeLayout所以是其父类的布局参数即RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.XXX
// // 注意其官方文档的描述:
// // Set the layout parameters associated with this view.
// // These supply parameters to the parent of this view specifying how it should be arranged.
// // 也就是说这个setLayoutParams()是给其父控件看的
// // 其实这也好理解:只有父类可以改变子View的位置布局.而不是说子View可以随意
// // 按照自己的想法摆放自己的位置,而不受父控件控制
// RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams
// =new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
// layoutParams.setMargins(280, 0, 0, 0);
// mTextView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
// //--------以上为测试1--------
//--------以下为测试2 在代码中设置控件居中--------
//注意:
//1 此处的new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h)参数w,h指的是
// 该控件在布局文件中所设置的宽和高
//2 同测试1中的描述
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams=
new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
layoutParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
mTextView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
//--------以下为测试2--------
}
}
}
package cn.testfixmargin;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.app.Activity;
/**
* Demo描述:
* 在代码中设置布局的属性
* 比如Margin和居中
*
* 注意事项:
* 参见代码中的详细注释
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView mTextView;
private Button mButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
init();
}
private void init(){
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(displayMetrics);
float density=displayMetrics.density;
float fontScale = displayMetrics.scaledDensity;
System.out.println("density="+density+",fontScale="+fontScale);
mTextView=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
mButton=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
}
private class OnClickListenerImpl implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// //--------以下为测试1 在代码中为控件设置Margin--------
// //注意:
// //1 此处的new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h)参数w,h指的是
// // 该控件的父控件的在布局文件中所设置的宽和高
// //2 此处必须使用RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT()
// // 因为其父类为RelativeLayout所以是其父类的布局参数即RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.XXX
// // 注意其官方文档的描述:
// // Set the layout parameters associated with this view.
// // These supply parameters to the parent of this view specifying how it should be arranged.
// // 也就是说这个setLayoutParams()是给其父控件看的
// // 其实这也好理解:只有父类可以改变子View的位置布局.而不是说子View可以随意
// // 按照自己的想法摆放自己的位置,而不受父控件控制
// RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams
// =new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
// layoutParams.setMargins(280, 0, 0, 0);
// mTextView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
// //--------以上为测试1--------
//--------以下为测试2 在代码中设置控件居中--------
//注意:
//1 此处的new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h)参数w,h指的是
// 该控件在布局文件中所设置的宽和高
//2 同测试1中的描述
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams=
new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
layoutParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
mTextView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
//--------以下为测试2--------
}
}
}
main.xml如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Click"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="补充:移动开发 , Android ,