poj1009 Edge Detection 解题报告
主要解决三问题1. 图像的存储
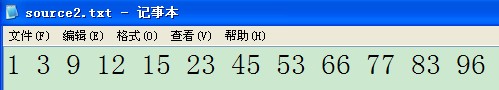
输入采用的是RLE编码,存储也采用类似的方式,但要做点变换。比如输入
7
15 4
100 15
25 2
175 2
25 5
175 2
25 5
0 0
经过变换,得到
7
15 4
100 19
25 21
175 23
25 28
175 30
25 35
其实就是把run length修改成了index分界值。这样做的好处是:要知道第n个像素的值,直接跟其中index分界值进行比较即可,简化了查找过程。
2. 每个像素edge值的计算
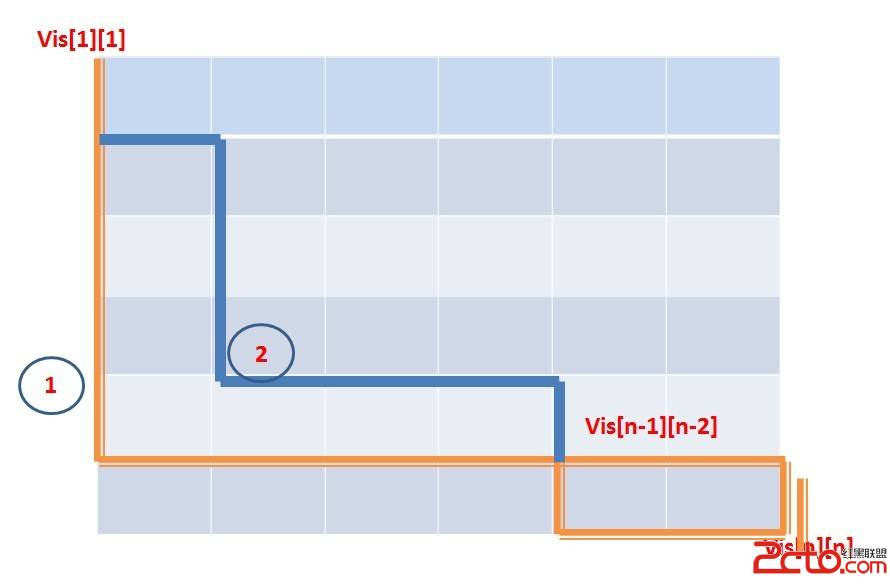
按照题目的要求,每个像素edge值是该像素与8邻域的最大差值。可以采用这样的处理方法:为8领域设置标志位,初始化均为true,表示邻域存在,然后根据像素的index判断它是否在图像的边界上,比如左上角的像素,其左边和上边的领域都不存在,根据不同的情况,对邻域的标志位进行更新。最后,只考虑标志位为true的领域,取它的值与当前像素值求差值,进而确定edge值。
3. 提速的技巧
逐像素进行处理一定会超时的,这里至少有两个提速的技巧。一是多行像素相同的情况,这时将有一连串值为0的edge;二是多列像素布局相同的情况,这时将有一连串相同edge值。下面是上述两种情况的例子
2
5 5000000
250 5000000
0 0
5000000
5 5000000
250 5000000
0 0
0
解题代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// struct BLOCK
struct BLOCK
{
short value;
int position;
};
const int N = 1005;
// CRLEImage
// class for run length encoded image
class CRLEImage
{
private:
BLOCK m_data[N];
int m_count;
int m_width;
public:
// constructor
CRLEImage() : m_count(0), m_width(0)
{
m_data[0].position = 0;
m_data[0].value = -1;
}
// Scan
bool Scan()
{
int width, value, run_length;
scanf("%d", &width);
if( width == 0 ) {
printf("0\n");
return false;
}
m_width = width;
int i = 1, index = 0;
while(true)
{
scanf("%d %d", &value, &run_length);
if( value == 0 && run_length == 0)
break;
index += run_length;
set_block(i, (short)value, index);
++i;
}
m_count = i-1;
return true;
}
// Process
void Process()
{
printf("%d\n", m_width);
short last_edge = calculate_edge(1, 1), edge;
int last_idx = 1, idx = 2;
for(int i = 1; i <= m_count; ++i)
{
while(idx <= m_data[i].position)
{
edge = calculate_edge(idx, i);
// if edge value change
if(edge != last_edge)
{
printf("%d %d\n", (int)last_edge, (idx - last_idx));
last_idx = idx;
last_edge = edge;
}
// same pixels in consecutive rows
if(last_edge == 0 && idx - m_data[i-1].position > m_width + 1
&& m_data[i].position - idx > m_width)
idx = m_data[i].position - m_width;
else ++idx;
// same pixels in consecutive columns
if(idx%m_width > 2 )
{
int same_length = m_width-1;
int idx_arr[3] = { idx-m_width-2, idx-2, idx+m_width-2 };
for( int j = 0; j < 3; ++j )
{
int location, temp;
search_pixel(idx_arr[j], i, (idx_arr[j]<idx), location);
if(location > 0)
{
temp = m_data[location].position - idx_arr[j];
if(temp
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,- 更多C/C++疑问解答:
- 关于c++的cout输出的问题。
- 在学校里学过C和C++,不过学的很一般,现在自学C#,会不会很难?
- 全国计算机二级C语言笔试题
- 已知某树有2个2度结点,3个3度结点,4个4度结点,问有几个叶子结点?
- c++数据结构内部排序问题,整数排序
- 2012九月计算机二级C语言全国题库,,急求急求
- 如果assert只有一个字符串作为参数,是什么意思呢?
- C语言中,哪些运算符具有左结合性,哪些具有右结合性,帮忙总结下,谢谢了!
- 为什么用结构体编写的程序输入是,0输不出来啊~~~
- 将IEEE—754的十六进制转化为十进制浮点类型,用C或C++都行,多谢各位大侠啊,非常感谢!
- 为什么这个程序求不出公式?
- 这个链表倒置的算法请大家分析下
- c语言函数库调用
- C语言unsigned int纠错
- C语言快排求解啊