Android 程式开发:(五)屏幕组件 —— 5.3 AbsoluteLayout绝对布局
使用AbsoluteLayout,可以指定它其中的子View的确切位置。观察如下main.xml中的代码:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
- <Button
- android:layout_width="188dp"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_x="126px"
- android:layout_y="361px"
- android:text="Button" />
- <Button
- android:layout_width="113dp"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_x="12px"
- android:layout_y="361px"
- android:text="Button" />
- </AbsoluteLayout>

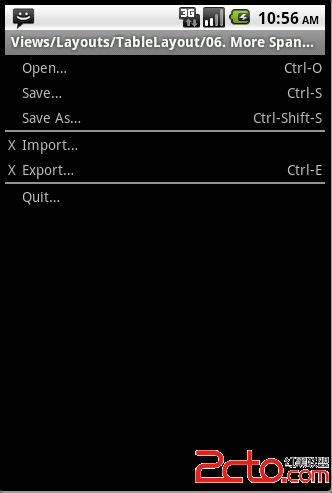
但当activity被绘制在一个高分辨率的屏幕上时,AbsoluteLayout就会出现某些问题。
下图是,在使用同样代码的前提下,高分辨率屏幕上显示出来的效果。

摘自 manoel的专栏
补充:移动开发 , Android ,