最大堆排序
其实堆排序就是对二叉树的一种操作,使得二叉树的左右孩子
节点都小于父节点。我使用的是数组的实现方式,
parent(i): return (i/2); //I的父节点下标,
left(i): return 2*i; //I的左子节点
right(i): return 2*i+1; //I的右子节点.
以上均为数组元素的标号位置,在存取元素时候,需要减一的。
举一个例子:
共六个节点。在数组中存储,每一个的编号如下:
|1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
二叉树的结构为
1
/ \
/ \
2 3
/ \ /
4 5 6
我使用的是递归的方法。
我首先从1节点开始递归。发现1节点的2、3子节点都有子节点,依次递归2,3。
2节点的子节点4、5没有子节点,对2、4、5进行堆排序。然后返回。
3节点的子节点6没有子节点,对3、6进行堆排序。然后返回。
1、2、3进行堆排序。首次堆排序完成。
1节点将是所有结果中的最值(最大或最小值)
然后将排序的数据减一,数组开始指针向后移动一位,返回第一步。直到排序数据为零。
(其实也可一将第一个数据,与最后一个数据交换,将要排序的数据减一,返回第一步也行的。)
下面是我写的代码,我在ubuntu中测试通过。与书中的方案不同,可能非最优方案,请大家谅解。一下是代码。
[cpp]
/*
*main function:maximum heap sort
*Author:Reage
*Blog: http://blog.csdn.net/rentiansheng
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*swap *p1 and p2 value
*/
void swap(int *p1, int * p2){
*p1 += *p2;
*p2 = *p1 - *p2;
*p1 -= *p2;
}
/*Left child node subscript.
*得到第i个节点的左孩子节点在数组中的下标
*注意节点从1开始计算
*/
int left(int i){
return (2 * i -1);
}
/*Right child node subscript
*得到第i个节点的右孩子节点在数组中的下标
*注意节点从1开始计算
*/
int right(int i){
return (2 * i);
}
/*Maximum heap sort
*最大堆的排序方法
*@parameter
* p:要进行排序的数组的其实坐标
* location:当前要进行最大堆运算的父节点是树中的第几个节点,从1开始算起
* count:(树)堆中的节点个数。
*/
void max_heap(int *p, int location, int count){
int l, r;
l = left(location);
r = right(location);
if(1 == count)return;
//当堆中第location的左孩子节点还有孩子节点。
//对location的左孩子节点递归最大堆的排序
if( 2 * (l + 1) <= count)
max_heap(p, l + 1, count);
//理由同上
if( 2 * (r + 1) <= count)
max_heap(p, r + 1, count);
//判断location的右孩子节点是否存,
if(r + 1 > count){
//当location的右孩子节点不存,只要对location和左孩子进行最大堆排序
if(p[l] > p[location - 1]){
swap(p + l, p + location - 1);
}
}
else {
//将location与左右孩子节点做最大堆排序
if(p[l] > p[r]){
if(p[l] > p[location - 1]){
swap(p + l, p + location - 1);
}
}
else{
if(p[r] > p[location - 1]){
swap(p + r, p + location - 1);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int count;
int i;
int *ptr;
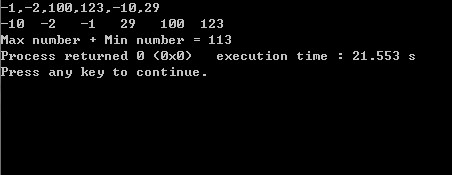
printf("input count:");
scanf("%d", &count);
ptr = (int *) malloc(count * sizeof(int));
memset(ptr, 0, count);
for(i = 0; i < count; i++)
scanf("%d", ptr+i);
printf("\n");
for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
max_heap(ptr + i, 1, count - i);
printf("%d ", ptr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/*
*main function:maximum heap sort
*Author:Reage
*Blog: http://blog.csdn.net/rentiansheng
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*swap *p1 and p2 value
*/
void swap(int *p1, int * p2){
*p1 += *p2;
*p2 = *p1 - *p2;
*p1 -= *p2;
}
/*Left child node subscript.
*得到第i个节点的左孩子节点在数组中的下标
*注意节点从1开始计算
*/
int left(int i){
return (2 * i -1);
}
/*Right child node subscript
*得到第i个节点的右孩子节点在数组中的下标
*注意节点从1开始计算
*/
int right(int i){
return (2 * i);
}
/*Maximum heap sort
*最大堆的排序方法
*@parameter
* p:要进行排序的数组的其实坐标
* location:当前要进行最大堆运算的父节点是树中的第几个节点,从1开始算起
* count:(树)堆中的节点个数。
*/
void max_heap(int *p, int location, int count){
int l, r;
l = left(location);
r = right(location);
if(1 == count)return;
//当堆中第location的左孩子节点还有孩子节点。
//对location的左孩子节点递归最大堆的排序
if( 2 * (l + 1) <= count)
max_heap(p, l + 1, count);
//理由同上
if( 2 * (r + 1) <= count)
max_heap(p, r + 1, count);
//判断location的右孩子节点是否存,
if(r + 1 > count){
//当location的右孩子节点不存,只要对locati
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,