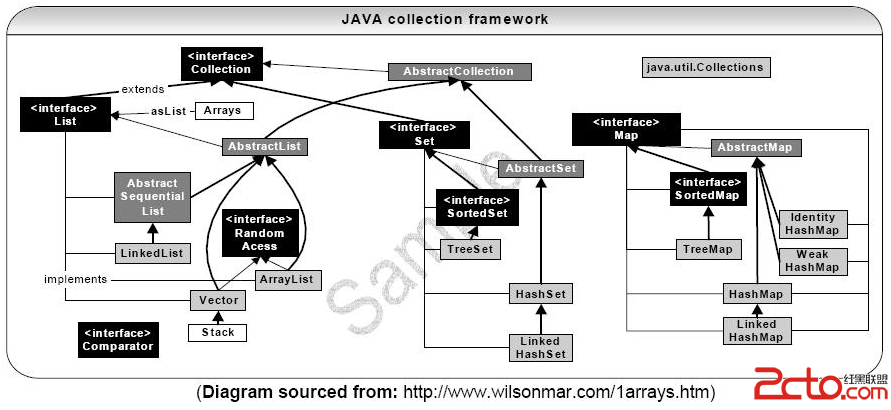
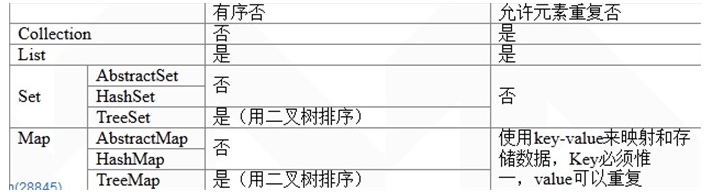
集合类:Collection--List, Set, Map
1.JAVA集合类最常用的集合有List, Set 和 MapList ------------LinkedList------------ArrayList------------Vector|-------StackSet------------HashSet|-------LinkedHashSet-------------SortedSet|------TreeSet对于它们的数据是否可以重复出现,是否有序,有如下特点:2.List2.1 ArrayListList的本质是array。 它在插入操作时会自动增加其大小,如下图的JDK 1. 6提供的源码:[java]private transient Object[] elementData; //elementData是一个数组public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;int oldCapacity = elementData.length;if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {Object oldData[] = elementData;int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1; //每次自动增加适量长度if (newCapacity < minCapacity)newCapacity = minCapacity;// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //拷贝旧数组到新数组,增加长度}}public void add(int index, E element) { //时间复杂度: O(n)if (index > size || index < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!!增加数组长度System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index); //再拷贝一次,留下index的位置给要插入的数据elementData[index] = element;size++;}[java]public E remove(int index) {RangeCheck(index);modCount++;E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its workreturn oldValue;}[java]/*** Returns the element at the specified position in this list.** @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E get(int index) {RangeCheck(index);return (E) elementData[index];}结构特点:ArrayList的特性跟数组很相似。元素有序可重复。查找操作:继承数组的特点,查找很快。修改操作:每次插入数据,必须移动其它数据,所以它在指定位置的插入操作较慢O(n),且浪费资源。线程安全:非线程同步。适用情况:适用于无平凡增删的情况。2.2 linkedList[java]private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);private transient int size = 0;/*** Constructs an empty list.*/public LinkedList() {header.next = header.previous = header;}[java]private E remove(Entry<E> e) {if (e == header)throw new NoSuchElementException();E result = e.element;e.previous.next = e.next;e.next.previous = e.previous;e.next = e.previous = null;e.element = null;size--;modCount++;return result;}[java]/*** Returns the indexed entry.*/private Entry<E> entry(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);Entry<E> e = header;if (index < (size >> 1)) {for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)e = e.next;} else {for (int i = size; i > index; i--)e = e.previous;}return e;}对于Linkedlist, 如果要查找指定位置的元素,它没有ArrayList快,必须从头或从尾一个一个地遍历。时间花费较大O(n).但是对于修改操作,如插入删除,同样花费O(n)先去找到这个index对应的元素,然后花费常量时间去修改链接。迭代器的使用会使LinkedList快捷很多。结构特点:链表。元素有序可重复。查找操作:查找速度不如ArrayList, 每次查找都得从头或从尾遍历。修改操作:速度快于ArrayList,不必移动其它元素。线程安全:非线程同步。适用情况:适用于有平凡增删的情况。2.3 Vector( Stack)Vector 非常类似于Arraylist. 但是最重要的区别是:Vector是线程同步的,也就是说Vector适合多线程操作。Stack继承自Vector,提供了一些pop,push, peek等用于Stack操作的方法。Stack也是线程安全的。结构特点:ArrayList。元素有序可重复。查找操作:查找速度补充:软件开发 , Java ,上一个:Map转Object
下一个:高效JDBC编程工具JadePool概述
- 更多JAVA疑问解答:
- java怎么在线读取ftp服务器上的文件内容
- 关于程序员的职业规划
- HTML和JSP矛盾吗?
- java小程序如何打包?
- java怎么split路径文件名?
- jsp+javaBean中Column 'ordersPrice' specified twice的错误
- Java TCP/IP Socket网络编程系列
- 大家来讨论一下我到底该用什么好?Swing 还是 JavaFX
- 关于Hibernate实体自身多对一的抓取问题
- 关于apache2+tomcat群集出现的问题
- spring 获取上下文问题
- SSH 导入导出excel 谁有这块的资料吗?
- Ext TreePanel 刷新问题
- springmvc 加载一个jsp页面执行多个方法 报404
- checkbox数组action怎么向页面传值