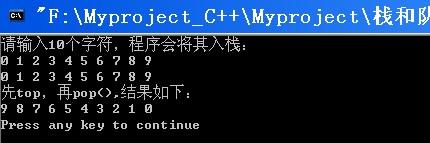
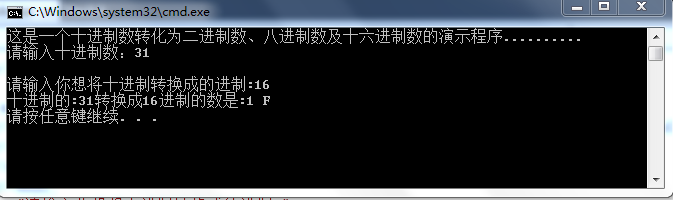
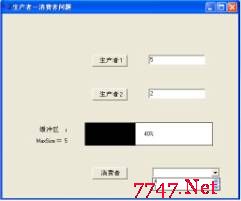
答案:多练习就好了转个例子给你#define NULL 0
#define TYPE struct stu
#define LEN sizeof(struct stu)
struct stu
{
int num;
int age;
struct stu *next;
};
TYPE * creat(int n)
{
struct stu *head,*pf,*pb;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
pb=(TYPE *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input Number and Age\n");
scanf("%d%d",&pb->num,&pb->age);
if(i==0)
pf=head=pb;
else pf->next=pb;
pb->next=NULL;
pf=pb;
}
return(head);
}
TYPE * delete(TYPE * head,int num)
{
TYPE *pf,*pb;
if(head==NULL)
{ printf("\nempty list!\n");
goto end;}
pb=head;
while (pb->num!=num && pb->next!=NULL)
{pf=pb;pb=pb->next;}
if(pb->num==num)
{ if(pb==head) head=pb->next;
else pf->next=pb->next;
printf("The node is deleted\n"); }
else
printf("The node not been found!\n");
end:
return head;
}
TYPE * insert(TYPE * head,TYPE * pi)
{
TYPE *pb ,*pf;
pb=head;
if(head==NULL)
{ head=pi;
pi->next=NULL; }
else
{
while((pi->num>pb->num)&&(pb->next!=NULL))
{ pf=pb;
pb=pb->next; }
if(pi->num<=pb->num)
{ if(head==pb) head=pi;
else pf->next=pi;
pi->next=pb; }
else
{ pb->next=pi;
pi->next=NULL; }
}
return head;
}
void print(TYPE * head)
{
printf("Number\t\tAge\n");
while(head!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t\t%d\n",head->num,head->age);
head=head->next;
}
}
main()
{
TYPE * head,*pnum;
int n,num;
printf("input number of node: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
head=creat(n);
print(head);
printf("Input the deleted number: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
head=delete(head,num);
print(head);
printf("Input the inserted number and age: ");
pnum=(TYPE *)malloc(LEN);
scanf("%d%d",&pnum->num,&pnum->age);
head=insert(head,pnum);
print(head);
}补充一点就是内存的分配和释放要小心!指针,就是指向下一个链表的指针,一定不能错了
- 更多C/C++疑问解答:
- 关于c++的cout输出的问题。
- 在学校里学过C和C++,不过学的很一般,现在自学C#,会不会很难?
- 全国计算机二级C语言笔试题
- 已知某树有2个2度结点,3个3度结点,4个4度结点,问有几个叶子结点?
- c++数据结构内部排序问题,整数排序
- 2012九月计算机二级C语言全国题库,,急求急求
- 如果assert只有一个字符串作为参数,是什么意思呢?
- C语言中,哪些运算符具有左结合性,哪些具有右结合性,帮忙总结下,谢谢了!
- 为什么用结构体编写的程序输入是,0输不出来啊~~~
- 将IEEE—754的十六进制转化为十进制浮点类型,用C或C++都行,多谢各位大侠啊,非常感谢!
- 为什么这个程序求不出公式?
- 这个链表倒置的算法请大家分析下
- c语言函数库调用
- C语言unsigned int纠错
- C语言快排求解啊