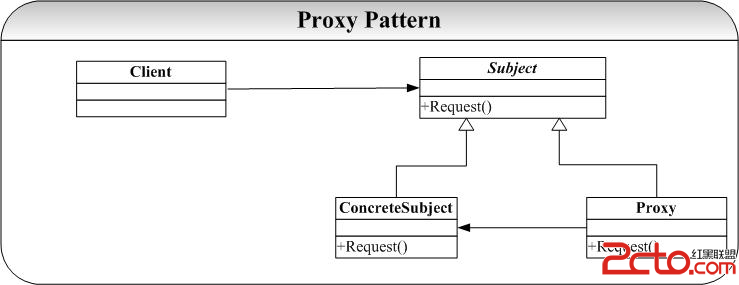
对于复杂的软件系统常常有一种处理手法,即增加一层间接层,从而使得系统获得一种更为灵活、满足特定需求的解决方案。在面向对象的系统中,有些对象由于某种原因,比如对象创建的开销很大,或者某些操作需要安全控制,或者需要进程外的访问等,直接访问会给使用者或者系统结构带来很多麻烦。
Proxy设计模式就是在不失去透明操作对象的同时,通过增加一层间接层来管理、控制这些对象特有的复杂性。
[cpp]
// Proxy.h
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class IEmployee
{
public:
virtual string get_name(int ID) = 0;
virtual int get_age(int ID) = 0;
virtual double get_salary(int ID) = 0;
public:
virtual ~IEmployee();
};
IEmployee::~IEmployee()
{
cout << "in the destructor of IEmployee..." << endl;
}
class Employee : public IEmployee
{
public:
string get_name(int ID);
int get_age(int ID);
double get_salary(int ID);
~Employee();
};
string Employee::get_name(int ID)
{
// ... 假定此处查询数据库,获得ID对应员工的姓名
string name = "tom";
return name;
}
int Employee::get_age(int ID)
{
// ... 假定此处查询数据库,获得ID对应员工的年龄
int age = 20;
return age;
}
double Employee::get_salary(int ID)
{
// ... 假定此处查询数据库,获得ID对应员工的工资
double salary = 100000.00;
return salary;
}
Employee::~Employee()
{
cout << "in the destructor of Employee..." << endl;
}
//代理
class EmployeeProxy : public IEmployee
{
public:
string get_name(int ID);
int get_age(int ID);
double get_salary(int ID);
~EmployeeProxy();
};
string EmployeeProxy::get_name(int ID)
{
// ...假定此处通过socket或者RPC等其他方式访问Employee中的get_name(int ID)方法,并接受相应的返回值
string name = "tom";
return name;
}
int EmployeeProxy::get_age(int ID)
{
// ...假定此处通过socket或者RPC等其他方式访问Employee中的get_age(int ID)方法,并接受相应的返回值
int age = 20;
return age;
}
double EmployeeProxy::get_salary(int ID)
{
// ...假定此处通过socket或者RPC等其他方式访问Employee中的get_salary(int ID)方法,并接受相应的返回值
double salary = 100000.00;
return salary;
}
EmployeeProxy::~EmployeeProxy()
{
cout << "in the destructor of EmployeeProxy..." << endl;
}
// Proxy.cpp
#include "Proxy.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
IEmployee *employee = new EmployeeProxy;
cout << employee->get_name(10) << endl;
cout << employee->get_age(10) << endl;
cout << employee->get_salary(10) << endl;
delete employee;
return 0;
}