Android 程式开发:(三)碎片简介 —— 3.1 动态添加Fragments
fragment的真正用处是在程序运行过程中动态地添加。
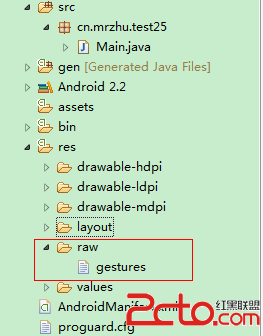
1.工程目录。

2.res/layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
</LinearLayout>
3.res/layout/fragment1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#00FF00"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/lblFragment1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment #1"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
4.res/layout/fragment2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#FFFE00"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment #2"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
5.Fragment1.java
package net.horsttnann.Fragments;
import net.horsttnann.Fragments.R;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// ---Inflate the layout for this fragment---
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
}
6.Fragment2.java
package net.horsttnann.Fragments;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// ---Inflate the layout for this fragment---
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
}
7.FragmentsActivity.java
package net.horsttnann.Fragments;
import net.horsttnann.Fragments.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Display;
import android.view.WindowManager;
public class FragmentsActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override www.zzzyk.com
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager
.beginTransaction();
// ---get the current display info---
WindowManager wm = getWindowManager();
Display d = wm.getDefaultDisplay();
if (d.getWidth() > d.getHeight()) {
// ---landscape mode---
Fragment1 fragment1 = new Fragment1();
// android.R.id.content refers to the content
// view of the activity
fragmentTransaction.replace(android.R.id.content, fragment1);
} else {
// ---portrait mode---
Fragment2 fragment2 = new Fragment2();
fragmentTransaction.replace(android.R.id.content, fragment2);
}
// ---add to the back stack---
fragmentTransaction.addToBackStack(null);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}
8.调试。
效果图:
补充:移动开发 , Android ,