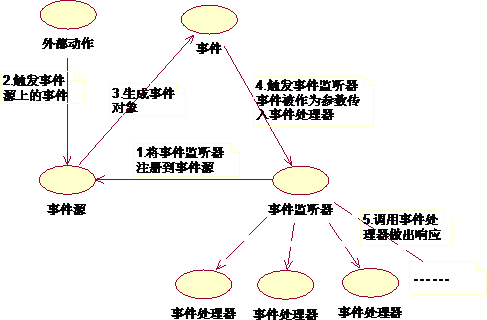
Android RecoverSystem 类
昨天开会讨论IP网络升级时,需要一个后台服务做升级检测及下载数据,最后在定义下载的数据存放位置及如何做开机标志时,突然发现一个很好用的上层java类对象。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\RecoverySystem.java
那么这个类做了什么事情呢?又是如何做到的。
RecoverySystem类,可以帮助我们调用系统还原等操作:
android.os.RecoverySystem,提供了如下静态方法
static void installPackage(Context context, File packageFile) //重启设备,安装一个更新包
static void rebootWipeUserData(Context context) //重启设备,清除用户数据分区类似恢复出厂设置
static String handleAftermath() 提供清除recover中相关文件,在开机广播中被调用
static void verifyPackage(File packageFile, RecoverySystem.ProgressListener listener, File deviceCertsZipFile) //验证加密签名的系统更新包在安装前,其中第二个数接口的具体定义为 android.os.RecoverySystem.ProgressListener 其中只有一个回调方法 abstract void onProgress(int progress) 来显示效验的进度。
下面具体看一下代码中是如何实现:
1、安装更新包:
/**
* Reboots the device in order to install the given update
* package.
* Requires the {@link android.Manifest.permission#REBOOT} permission.
*
* @param context the Context to use
* @param packageFile the update package to install. Must be on
* a partition mountable by recovery. (The set of partitions
* known to recovery may vary from device to device. Generally,
* /cache and /data are safe.)
*
* @throws IOException if writing the recovery command file
* fails, or if the reboot itself fails.
*/
public static void installPackage(Context context, File packageFile)
throws IOException {
String filename = packageFile.getCanonicalPath();
Log.w(TAG, "!!! REBOOTING TO INSTALL " + filename + " !!!");
String arg = "--update_package=" + filename;
bootCommand(context, arg); // 都是调用了这个函数
}
/**
* Reboot into the recovery system with the supplied argument.
* @param arg to pass to the recovery utility.
* @throws IOException if something goes wrong.
*/
private static void bootCommand(Context context, String arg) throws IOException {
RECOVERY_DIR.mkdirs(); // In case we need it
COMMAND_FILE.delete(); // In case it's not writable
LOG_FILE.delete();
FileWriter command = new FileWriter(COMMAND_FILE); // 写命令写入到recover中
try {
command.write(arg);
command.write("\n");
} finally {
command.close();
}
// Having written the command file, go ahead and reboot 系统重启
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) context.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
pm.reboot("recovery");
throw new IOException("Reboot failed (no permissions?)");
}
/**
* Reboots the device in order to install the given update
* package.
* Requires the {@link android.Manifest.permission#REBOOT} permission.
*
* @param context the Context to use
* @param packageFile the update package to install. Must be on
* a partition mountable by recovery. (The set of partitions
* known to recovery may vary from device to device. Generally,
* /cache and /data are safe.)
*
* @throws IOException if writing the recovery command file
* fails, or if the reboot itself fails.
*/
public static void installPackage(Context context, File packageFile)
throws IOException {
String filename = packageFile.getCanonicalPath();
Log.w(TAG, "!!! REBOOTING TO INSTALL " + filename + " !!!");
String arg = "--update_package=" + filename;
bootCommand(context, arg); // 都是调用了这个函数
}
/**
* Reboot into the recovery system with the supplied argument.
* @param arg to pass to the recovery utility.
* @throws IOException if something goes wrong.
*/
private static void bootCommand(Context context, String arg) throws IOException {
RECOVERY_DIR.mkdirs(); // In case we need it
COMMAND_FILE.delete(); // In case it's not writable
LOG_FILE.delete();
FileWriter command = new FileWriter(COMMAND_FILE); // 写命令写入到recover中
try {
command.write(arg);
command.write("\n");
} finally {
command.close();
}
// Having written the command file, go ahead and reboot 系统重启
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) context.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
pm.reboot("recovery");
throw new IOException("Reboot failed (no permissions?)");
}
2、出厂恢复
/**
* Reboots the device and wipes the user data partition. This is
* sometimes called a "factory reset", which is something of a
* misnomer because the system partition is not restored to its
* factory state.
* Requires the {@link android.Manifest.permission#REBOOT} permission.
*
* @param context the Context to use
*
* @throws IOException if writing the recovery command file
* fails, or if the reboot itself fails.
*/
public static void rebootWipeUserData(Context context) throws IOException {
final ConditionVariable condition = new ConditionVariable();
Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.MASTER_CLEAR_NOTIFICATION");
context.sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, android.Manifest.permission.MASTER_CLEAR,
new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
condition.open();
}
}, null, 0, null, null);
// Block until the ordered broadcast has completed.
condition.block();
bootCommand(context, "--wipe_data");
}
/**
* Reboot into the recovery system to wipe the /cache partition.
* @throws IOException if something goes wrong.
*/
public static void rebootWipeCache(Context context) throws IOException {
bootCommand(context, "--wipe_cache");
}
/**
* Reboots the device and wipes the user data partition. This is
* sometimes called a "factory reset", which is something of a
* misnomer because the system partition is not restored to its
* factory state.
* Requires the {@link android.Manifest.permission#REBOOT} permission.
*
* @param context the Context to use
*
* @throws IOException if writing the recovery command file
* fails, or if the reboot itself fails.
*/
public static void rebootWipeUserData(Context context) throws IOException {
final ConditionVariable condition = new ConditionVariable();
Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.MASTER_CLEAR_NOTIFICATION");
context.sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, android.Manifest.permission.MASTER_CLEAR,
new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
condition.open();
}
}, null, 0, null, null);
// Block until the ordered broadcast has completed.
condition.block();
bootCommand(context, "--wipe_data");
}
/**
* Reboot into the recovery system to wipe the /cache partition.
* @throws IOException if something goes wrong.
*/
public static void rebootWipeCache(Context context) throws IOException {
bootCommand(context, "--wipe_cache");
}
3、验证签名
&n
补充:移动开发 , Android ,