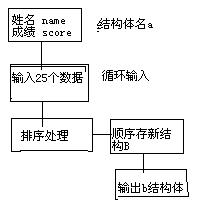
关于C++多态的理解
类的多态特性是支持面向对象的语言最主要的特性,有过非面向对象语言开发经历的人,通常对这一章节的内容会觉得不习惯,因为很多人错误的认为,支持类的封装的语言就是支持面向对象的,其实不然,Visual BASIC 6.0 是典型的非面向对象的开发语言,但是它的确是支持类,支持类并不能说明就是支持面向对象,能够解决多态问题的语言,才是真正支持面向对象的开发的语言,所以务必提醒有过其它非面向对象语言基础的读者注意!
多态的这个概念稍微有点模糊,如果想在一开始就想用清晰用语言描述它,让读者能够明白,似乎不太现实,所以我们先看如下代码:
//例程1
01
#include <iostream>
02
using namespace std;
03
04
class Vehicle
05
{
06
public:
07
Vehicle(float speed,int total)
08
{
09
Vehicle::speed=speed;
10
Vehicle::total=total;
11
}
12
void ShowMember()
13
{
14
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<endl;
15
}
16
protected:
17
float speed;
18
int total;
19
};
20
class Car:public Vehicle
21
{
22
public:
23
Car(int aird,float speed,int total):Vehicle(speed,total)
24
{
25
Car::aird=aird;
26
}
void ShowMember() 但是在实际工作中,很可能会碰到对象所属类不清的情况,下面我们来看一下派生类成员作为函数参数传递的例子,代码如下:
//例程2
01
#include <iostream>
02
using namespace std;
03
04
class Vehicle
05
{
06
public:
07
Vehicle(float speed,int total)
08
{
09
Vehicle::speed=speed;
10
Vehicle::total=total;
11
}
12
void ShowMember()
13
{
14
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<endl;
15
}
16
protected:
17
float speed;
18
int total;
19
};
20
class Car:public Vehicle
21
{
22
public:
23
Car(int aird,float speed,int total):Vehicle(speed,total)
24
{
25
Car::aird=aird;
26
}
27
void ShowMember()
28
{
29
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<"|"<<aird<<endl;
30
}
31
protected:
32
int aird;
33
};
34
35
void test(Vehicle &temp)
36
{
37
temp.ShowMember();
38
}
39
40
void main()
41
{
42
Vehicle a(120,4);
43
Car b(180,110,4);
44
test(a);
45
test(b);
46
cin.get();
47
}
例子中,对象a与b分辨是基类和派生类的对象,而函数test的形参却只是Vehicle类的引用,按照类继承的特点,系统把Car类对象看做是一个 Vehicle类对象,因为Car类的覆盖范围包含Vehicle类,所以test函数的定义并没有错误,我们想利用test函数达到的目的是,传递不同 类对象的引用,分别调用不同类的,重载了的,ShowMember成员函数,但是程序的运行结果却出乎人们的意料,系统分不清楚传递过来的基类对象还是派生类对象,无论是基类对象还是派生类对象调用的都是基类的ShowMember成员函数。
01
{
02
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<"|"<<aird<<endl;
03
}
04
protected:
05
int aird;
06
};
07
08
void main()
09
{
10
Vehicle a(120,4);
11
a.ShowMember();
12
Car b(180,110,4);
13
b.ShowMember();
14
cin.get();
15
}
在c++中是允许派生类重载基类成员函数的,对于类的重载来说,明确的,不同类的对象,调用其类的成员函数的时候,系统是知道如何找到其类的同名成员, 上面代码中的a.ShowMember();,即调用的是Vehicle::ShowMember(),b.ShowMember();,即调用的是 Car::ShowMemeber();。
但是在实际工作中,很可能会碰到对象所属类不清的情况,下面我们来看一下派生类成员作为函数参数传递的例子,代码如下:
//例程2
01
#include <iostream>
02
using namespace std;
03
04
class Vehicle
05
{
06
public:
07
Vehicle(float speed,int total)
08
{
09
Vehicle::speed=speed;
10
Vehicle::total=total;
11
}
12
void ShowMember()
13
{
14
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<endl;
15
}
16
protected:
17
float speed;
18
int total;
19
};
20
class Car:public Vehicle
21
{
22
public:
23
Car(int aird,float speed,int total):Vehicle(speed,total)
24
{
25
Car::aird=aird;
26
}
27
void ShowMember()
28
{
29
cout<<speed<<"|"<<total<<"|"<<aird<<endl;
30
}
31
protected:
32
int aird;
33
};
34
35
void test(Vehicle &temp)
36
{
37
&nb
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,