Android 4.0 Launcher源码分析系列(二)
这一节我们看看整个Laucher的入口点,同时Laucher在加载了它的布局文件Laucher.xml时都干了些什么。我们在源代码中可以找到LauncherApplication, 它继承了Application类,当整个Launcher启动时,它就是整个程序的入口。我们先来看它们在AndroidManifest.xml中是怎么配置的。
1. <application
2. android:name="com.android.launcher2.LauncherApplication"
3. android:label="@string/application_name"
4. android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_home"
5. android:hardwareAccelerated="@bool/config_hardwareAccelerated"
6. android:largeHeap="@bool/config_largeHeap">
首先通过android:name指定了整个Launcher的Application也就是入口是在 com.android.launcher2.LauncherApplication这个路径下,android:lable指定了桌面的名字是叫 Launcher,如果要改名字就改values文件夹的string.xml中的相应属性就可以了。android:icon指定了Laucher的图标,这个图标可以在应用程序管理器中看见,如下图所示,是个可爱机器人住在一个小房子里面,如果需要更改Laucher的图片,重新设置这个属性就可以了。
android:hardwareAccelerated="@bool/config_hardwareAccelerated" 指定了整个应用程序是启用硬件加速的,这样整个应用程序的运行速度会更快。
android:largeHeap="@bool/config_largeHeap" 指定了应用程序使用了大的堆内存,能在一定程度上避免,对内存out of memory错误的出现。我们可以在values文件夹的config.xml中看到对是否启用硬件加速和大内存的配置。如下所示:
1. <bool name="config_hardwareAccelerated">true</bool>
2. <bool name="config_largeHeap">false</bool>
在Application中onCreate()方法通过:sIsScreenLarge = screenSize == Configuration.SCREENLAYOUT_SIZE_LARGE || screenSize == Configuration.SCREENLAYOUT_SIZE_XLARGE; 和sScreenDensity = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;来判断是否是大屏幕,同时得到它的屏幕密度。同时通过mIconCache = new IconCache(this); 来设置了应用程序的图标的cache,然后申明了LauncherModel,mModel = new LauncherModel(this, mIconCache); LauncherModel主要用于加载桌面的图标、插件和文件夹,同时LaucherModel是一个广播接收器,在程序包发生改变、区域、或者配置文件发生改变时,都会发送广播给LaucherModel,LaucherModel会根据不同的广播来做相应加载操作,此部分会在后面做详细介绍。
在LauncherApplication完成初始化工作之后,我们就来到了Launcher.java的onCreate()方法,同样是启动桌面时的一系列初始化工作。
首先需要注意的是在加载launcher布局文件时的一个TraceView的调试方法,它能够对在他们之间的方法进行图形化的性能分析,并且能够具体到method 代码如下:
1. if (PROFILE_STARTUP) {
2. android.os.Debug.startMethodTracing(
3. Environment.getDataDirectory() + "/data/com.android.launcher/launcher");
4. }
5. if (PROFILE_STARTUP) {
6. android.os.Debug.stopMethodTracing();
7. }
我指定的生成性能分析的路径是:/data/data/com.android.launcher/launcher,启动launcher后我们会发现在指定的目录下生成了launcher.trace文件,如下图所示:

把launcher.trace文件通过DDMS pull到电脑上,在SDK的tools目录里,执行traceview工具来打开launcher.trace .如下图所示:
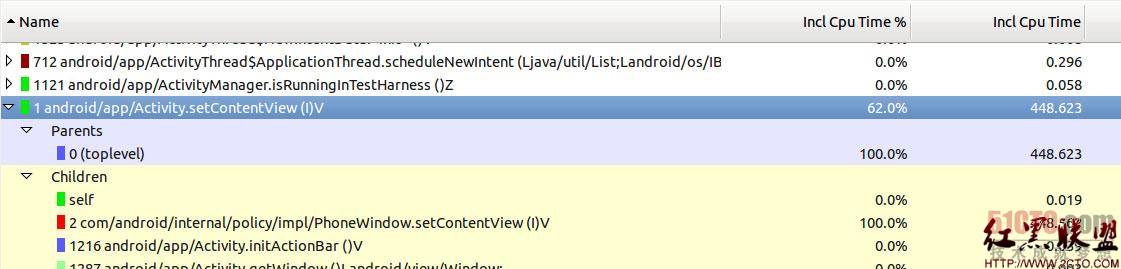
点击查看大图
可以看到setContentView使用了448.623ms,占整个跟踪代码时间的62%,所以说在加载布局文件时,肯定经过了一系列的加载运算,我们接着分析。
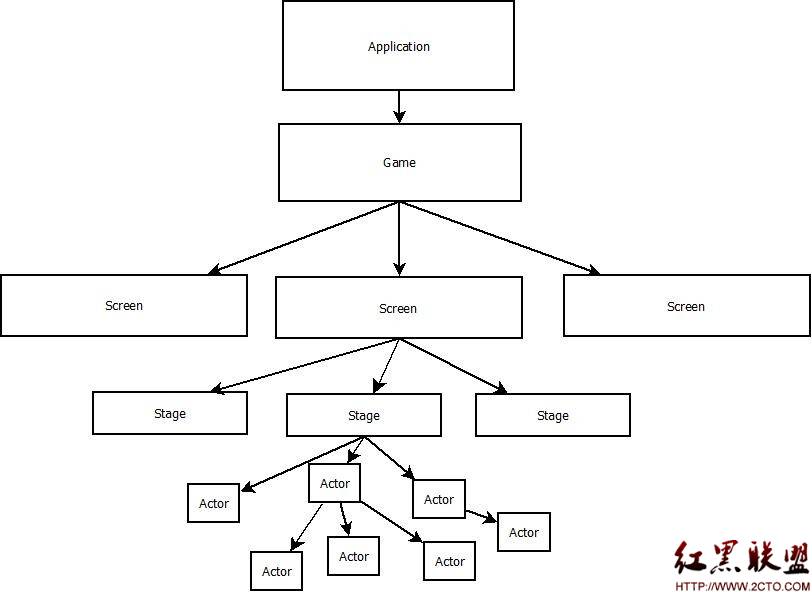
当加载launcher布局文件的过程时,最为关键的时对整个workspace的加载,workspace是一个自定义组件,它的继承关系如下所示,可以看到Workspace实际上也是一个ViewGroup,可以加入其他控件。

当ViewGroup组件进行加载的时候首先会读取本控件对应的XML文件,然后Framework层会执行它的onMeasure()方法,根据它所包含的子控件大小来计算出整个控件要在屏幕上占的大小。Workspace重写了ViewGroup的onMeasure方法(在PagedView中),在workspace中是对5个子CellLayout进行测量,的方法如下, 具体含义请看注释:
1. @Override
2. protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
3. if (!mIsDataReady) {
4. super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
5. return;
6. }
7. //得到宽度的模式(在配置文件中对应的是match_parent 或者 wrap_content)和其大小
8. final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
9. final int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
10. //宽度必须是match_parent,否则会抛出异常。
11. if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
12. throw new IllegalStateException("Workspace can only be used in EXACTLY mode.");
13. }
14.
15. /* Allow the height to be set as WRAP_CONTENT. This allows the particular case
16. * of the All apps view on XLarge displays to not take up more space then it needs. Width
17. * is still not allowed to be set as WRAP_CONTENT since many parts of the code expect
18. * each page to have the same width.
19. */
20. //高度允许是wrap_content,因为在大屏幕的情况下,会占了多余的位置
21. final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
22. int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
23. int maxChildHeight = 0;
24. //得到在竖值方向上和水平方向上的Padding
25. final int verticalPadding = mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
26. final int horizontalPadding = mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight;
27.
28.
29. // The children are given the same width and height as the workspace
30. // unless they were set to WRAP_CONTENT
31. if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "PagedView.onMeasure(): " + widthSize + ", " + heightSize + " mPaddingTop="+mPaddingTop + " mPaddingBottom="+mPaddingBottom);
32. final int childCount = getChildCount();
33. //对workspace的子View进行遍历,从而对它的几个子view进行测量。
34. for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
35. // disallowing padding in paged view (just pass 0)
36. &nb
补充:移动开发 , Android ,