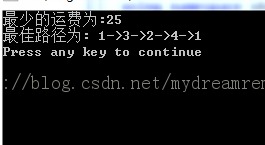
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<bitset>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#define FF(i, a, b) for(int i=a; i<b; i++)
#define FD(i, a, b) for(int i=a; i>=b; i--)
#define REP(i, n) for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
#define CLR(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define debug puts("**debug**")
#define LL long long
#define PB push_back
#define MP make_pair
#define eps 1e-8
using namespace std;
int dcmp(double x) { if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1; }
struct Point3 {
double x, y, z;
Point3(double x=0, double y=0, double z=0):x(x),y(y),z(z) { }
};
typedef Point3 Vector3;
Vector3 operator + (const Vector3& A, const Vector3& B) { return Vector3(A.x+B.x, A.y+B.y, A.z+B.z); }
Vector3 operator - (const Point3& A, const Point3& B) { return Vector3(A.x-B.x, A.y-B.y, A.z-B.z); }
Vector3 operator * (const Vector3& A, double p) { return Vector3(A.x*p, A.y*p, A.z*p); }
Vector3 operator / (const Vector3& A, double p) { return Vector3(A.x/p, A.y/p, A.z/p); }
bool operator == (const Point3& a, const Point3& b) {
return dcmp(a.x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y-b.y) == 0 && dcmp(a.z-b.z) == 0;
}
Point3 read_point3() {
Point3 p;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &p.x, &p.y, &p.z);
return p;
}
double Dot(const Vector3& A, const Vector3& B) { return A.x*B.x + A.y*B.y + A.z*B.z; }
double Length(const Vector3& A) { return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); }
double Angle(const Vector3& A, const Vector3& B) { return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B)); }
Vector3 Cross(const Vector3& A, const Vector3& B) { return Vector3(A.y*B.z - A.z*B.y, A.z*B.x - A.x*B.z, A.x*B.y - A.y*B.x); }
double Area2(const Point3& A, const Point3& B, const Point3& C) { return Length(Cross(B-A, C-A)); }
double Volume6(const Point3& A, const Point3& B, const Point3& C, const Point3& D) { return Dot(D-A, Cross(B-A, C-A)); }
Point3 Centroid(const Point3& A, const Point3& B, const Point3& C, const Point3& D) { return (A + B + C + D)/4.0; }
double rand01() { return rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; }
double randeps() { return (rand01() - 0.5) * eps; }
Point3 add_noise(const Point3& p) {
return Point3(p.x + randeps(), p.y + randeps(), p.z + randeps());
}
struct Face {
int v[3];
Face(int a, int b, int c) { v[0] = a; v[1] = b; v[2] = c; }
Vector3 Normal(const vector<Point3>& P) const {
return Cross(P[v[1]]-P[v[0]], P[v[2]]-P[v[0]]);
}
// f是否能看见P[i]
int CanSee(const vector<Point3>& P, int i) const {
return Dot(P[i]-P[v[0]], Normal(P)) > 0;
}
};
// 增量法求三维凸包
// 注意:没有考虑各种特殊情况(如四点共面)。实践中,请在调用前对输入点进行微小扰动
vector<Face> CH3D(const vector<Point3>& P) {
int n = P.size();
vector<vector<int> > vis(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) vis[i].resize(n);
vector<Face> cur;
cur.push_back(Face(0, 1, 2)); // 由于已经进行扰动,前三个点不共线
cur.push_back(Face(2, 1, 0));
for(int i = 3; i < n; i++) {
vector<Face> next;
// 计算每条边的“左面”的可见性
for(int j = 0; j < cur.size(); j++) {
Face& f = cur[j];
int res = f.CanSee(P, i);
if(!res) next.push_back(f);
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++) vis[f.v[k]][f.v[(k+1)%3]] = res;
}
for(int j = 0; j < cur.size(); j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
int a = cur[j].v[k], b = cur[j].v[(k+1)%3];
if(vis[a][b] != vis[b][a] && vis[a][b]) // (a,b)是分界线,左边对P[i]可见
next.push_back(Face(a, b, i));
}
cur = next;
}
return cur;
}
struct ConvexPolyhedron {
int n;
vector<Point3> P, P2;
vector<Face> faces;
bool read() {
if(scanf("%d", &n) != 1) return false;
P.resize(n);
P2.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { P[i] = read_point3(); P2[i] = add_noise(P[i]); }
faces = CH3D(P2);
return true;
}
Point3 centroid() {
Point3 C = P[0];
double totv = 0;
Point3 tot(0,0,0);
for(int i = 0; i < faces.size(); i++) {
Point3 p1 = P[faces[i].v[0]], p2 = P[faces[i].v[1]], p3 = P[faces[i].v[2]];
double v = -Volume6(p1, p2, p3, C);
totv += v;
tot = tot + Centroid(p1, p2, p3, C)*v;
}
return tot / totv;
}
double mindist(Point3 C) {
double ans = 1e30;
for(int i = 0; i < faces.size(); i++) {
Point3 p1 = P[faces[i].v[0]], p2 = P[faces[i].v[1]], p3 = P[faces[i].v[2]];
ans = min(ans, fabs(-Volume6(p1, p2, p3, C) / Area2(p1, p2, p3)));
}
return ans;
}
}P1;
int main()
{
int n, m;
ConvexPolyhedron P1, P2;
while(P1.read()) {
Point3 C1 = P1.centroid();
double d1 = P1.mindist(C1);
printf("%.3f\n", d1);
}
return 0;
}