OCI : do NOT debug on TWO different wind
这两天在使用Oracle,好久没用了,生疏了很多。。。
开始使用occi访问,可以是代码很精简,因为occi封装的还是很好的,使用起来跟mysql++很类似,也不知道他们谁参考谁的,反正用起来就是很简单。
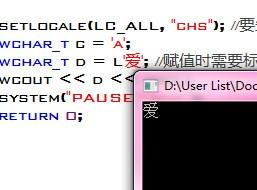
联调起来却碰到了个易做图烦,本来说好是Linux平台的,等调试时却要换到Windows上,问题来了,occi11跟VC9似乎不合拍,Environment初始就出错,折腾了很久,最终只有放弃了。测试下oci,嗯,可以用。。。
于是,晚上一狠心,自己封装oci,模仿occi做个ocipp来,好用了。。。
这里说个调试过程中一件丢脸的事情--使用ocipp访问同时,打开SQLPlus窗口,进行对比测试,select语句很好用,但到update/delete语句时,程序卡死在execute调用中,想了很久,也尝试了很久,到了凌晨1点半,一直卡死,人近疯狂,突然想起,SQLPlus窗口下的语句默认需要自己输入commit语句提交的,而ocipp用的是Auto-commit方式,两者应该有冲突的。于是在SQLPlus输入个commit,一切pass。。。
所以,记得,调试oci接口时,不要开两个窗口,会死人的。。。
下面是ocipp代码,仅供看热闹,不推荐使用,因为除了有危险外,也很有限制,比如ocipp仅支持string类型的define和bind,因为,我的代码仅需要这一种类型。。。
ocipp.h
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "oci.h"
namespace ocipp
{
class Exception
{
public:
Exception(int code, const std::string& msg);
Exception(int code, OCIError *err, const std::string& msg);
void show(std::ostream& os) const;
protected:
void getError(int code);
void getError(int code, OCIError *err);
protected:
int _code;
std::string _msg;
};
class Connection;
class Environment
{
public:
Environment(unsigned int mode = OCI_DEFAULT);
virtual ~Environment();
Connection* makeConnection(const std::string& user, const std::string& passwd, const std::string& server = "");
void destroyConnection(Connection* conn);
OCIEnv *getEnv() { return _env; }
OCIError *getError() { return _err; }
private:
void makeEnvironment(unsigned int mode);
protected:
OCIEnv *_env;
OCIError *_err;
};
class Statement;
class Connection
{
friend class Environment;
protected:
Connection(Environment* env);
virtual ~Connection() {}
public:
Statement *makeStatement(const std::string& sql);
void destroyStatement(Statement* stmt);
Environment *getEnvironment() { return _env; }
OCISvcCtx *getSvc() { return _svc; }
private:
Environment *_env;
protected:
OCIServer *_srv;
OCISvcCtx *_svc;
OCISession *_auth;
};
class Statement
{
friend class Connection;
protected:
static const size_t BUF_SIZE = 256;
struct TDefData
{
TDefData(std::string& val)
: str(&val), buf(NULL)
{
buf = new char[BUF_SIZE];
}
std::string* str;
char* buf;
};
typedef std::vector<TDefData> TDefVector;
protected:
Statement(Connection* conn);
virtual ~Statement() {}
void syncDefVector();
void freeDefVector();
public:
int bindString(unsigned int pos, const std::string& val);
int defineString(unsigned int pos, std::string& val);
int execute();
int getNext();
private:
Connection *_conn;
protected:
O CIStmt *_stmt;
TDefVector _vctDef;
};
}
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const ocipp::Exception& e);
ocipp.cpp
#include "ocipp.h"
namespace ocipp
{
Exception::Exception(int code, const std::string &msg)
: _code(code)
, _msg(msg)
{
getError(code);
}
Exception::Exception(int code, OCIError* err, const std::string &msg)
: _code(code)
, _msg(msg)
{
getError(code, err);
}
void Exception::getError(int code)
{
switch(code)
{
case OCI_SUCCESS:
_msg = "(OCI_SUCCESS) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO:
_msg = "(OCI_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_NEED_DATA:
_msg = "(OCI_NEED_DATA) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_NO_DATA:
_msg = "(OCI_NODATA) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_ERROR:
_msg = "(OCI_ERROR) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_INVALID_HANDLE:
_msg = "(OCI_INVALID_HANDLE) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_STILL_EXECUTING:
_msg = "(OCI_STILL_EXECUTE) - " + _msg;
break;
case OCI_CONTINUE:
_msg = "(OCI_CONTINUE) - " + _msg;
break;
default:
_msg = "(UNKNOWN) - " + _msg;
}
}
void Exception::getError(int code, OCIError *err)
{
getError(code);
//if(code == OCI_ERROR)
{
char buf[512];
OCIErrorGet((void*)err, 1, NULL, &code, (OraText*)buf, sizeof(buf), OCI_HTYPE_ERROR);
_msg += "::";
_msg += buf;
}
}
void Exception::show(std::ostream &os) const
{
os << "[" << _code << "]" << _msg;
}
/**/////
Environment::Environment(unsigned int mode)
: _env(NULL)
, _err(NULL)
{
makeEnvironment(mode);
}
Environment::~Environment()
{
if(_err != NULL)
{
OCIHandleFree((void*)_err, OCI_HTYPE_ERROR);
_err = NULL;
}
if(_env != NULL)
{
OCIHandleFree((void*)
补充:软件开发 , C语言 ,