Vaadin Web应用开发教程(6):使用资源
Web应用使用多种资源,比如图像或是供下载的文件。Vaadin中的Embeded UI通常显示图像而Link提供可供下载的文件,其它的UI组件,比如TabSheet可以使用图标资源。
Web服务器通常无需Application对象的帮助就可以处理对静态资源的请求,对于一些可以动态生成的资源(图像,或文件等)Application则需动态创建这些资源。Vaadin支持多种资源类型的创建,比如动态创建文件。
下图为Vaadin提供的资源管理的接口类:
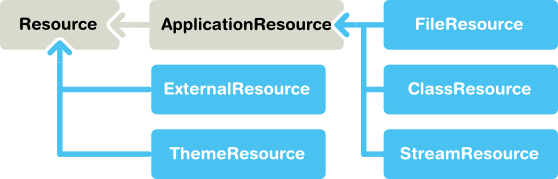
Vaadin提供两大类资源接口,一为通用的资源Resource接口,另外一个为特定的应用程序资源ApplicationResource.
应用程序资源ApplicationResource的管理是通过Application对象来完成的。当创建该类资源时,Application对象做为构造函数的参数传入。构造函数使用addResource向Application对象注册该资源。
Application对象提供URI来管理对资源的访问。URI的基本格式为 “APP/”+resourceid+”/”+filename, 其中resourceid 为自动生成的用于唯一指定资源的ID号。
文件资源(File Resources) 文件资源指文件系统的文件,一般可以分为两种,供显示的图像和供下载的文件。 可以使用标准的java.io.File API来访问文件。可以使用相对路径或是绝对路径来访问某个文件。
包资源 (Class Loader Resources) 随打包文件.war 打包的文件中可以包含图像等资源,此时可以通过ClassLoader 来访问这些资源文件。比如下面代码使用ClassLoader 来访问打包文件中的一个图像资源。
[java]
mainwindow.addComponent(new Embedded ("",
new ClassResource("smiley.jpg",
mainwindow.getApplication())));
mainwindow.addComponent(new Embedded ("",
new ClassResource("smiley.jpg",
mainwindow.getApplication())));
主题资源 (Theme Resources) 由类ThemeResource 管理的主题资源文件,通常为一些图像文件。Vaadin的主题在项目中存放在目录VAADIN/themes/themename 下。下面代码片段用来获取当前主题的一个图像资源。
[java]
// A theme resource in the current theme ("book-examples")
// Located in: VAADIN/themes/book-examples/img/themeimage.png
ThemeResource resource = new ThemeResource("img/themeimage.png");
// Use the resource
Embedded image = new Embedded("My Theme Image", resource);
// A theme resource in the current theme ("book-examples")
// Located in: VAADIN/themes/book-examples/img/themeimage.png
ThemeResource resource = new ThemeResource("img/themeimage.png");
// Use the resource
Embedded image = new Embedded("My Theme Image", resource);
对应项目资源目录如下图:

关于资源的详细使用将在后面的文章中介绍。
流资源(Stream Resources) 使用流资源允许应用动态创建资源。比如动态创建图表。可以通过实现StreamResource.StreamSource 接口来定义一个流资源。这个方法返回一个InputStream。
下面的例子动态创建一个PNG图像。
[java]
import java.awt.image.*;
public class MyImageSource
implements StreamResource.StreamSource {
ByteArrayOutputStream imagebuffer = null;
int reloads = 0;
/* We need to implement this method that returns
* the resource as a stream. */
public InputStream getStream () {
/* Create an image and draw something on it. */
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage (200, 200,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics drawable = image.getGraphics();
drawable.setColor(Color.lightGray);
drawable.fillRect(0,0,200,200);
drawable.setColor(Color.yellow);
drawable.fillOval(25,25,150,150);
drawable.setColor(Color.blue);
drawable.drawRect(0,0,199,199);
drawable.setColor(Color.black);
drawable.drawString("Reloads="+reloads, 75, 100);
reloads++;
try {
/* Write the image to a buffer. */
imagebuffer = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(image, "png", imagebuffer);
/* Return a stream from the buffer. */
return new ByteArrayInputStream(
imagebuffer.toByteArray());
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
}
import java.awt.image.*;
public class MyImageSource
implements StreamResource.StreamSource {
ByteArrayOutputStream imagebuffer = null;
int reloads = 0;
/* We need to implement this method that returns
* the resource as a stream. */
public InputStream getStream () {
/* Create an image and draw something on it. */
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage (200, 200,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics drawable = image.getGraphics();
drawable.setColor(Color.lightGray);
drawable.fillRect(0,0,200,200);
drawable.setColor(Color.yellow);
drawable.fillOval(25,25,150,150);
drawable.setColor(Color.blue);
drawable.drawRect(0,0,199,199);
drawable.se
补充:Web开发 , 其他 ,