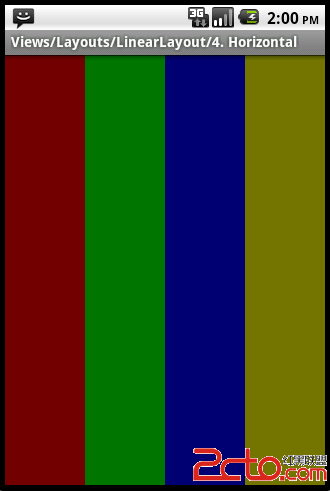
Android ApiDemos示例解析(144):Views->Layouts->LinearLayout->4. Horizontal
本例介绍了LinearLayout 水平布局的基本用法:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=”horizontal”
android:layout_width=”match_parent”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”>
<TextView
android:background=”@drawable/red”
android:layout_width=”0dip”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:layout_weight=”1″/>
<TextView
android:background=”@drawable/green”
android:layout_width=”0dip”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:layout_weight=”1″/>
<TextView
android:background=”@drawable/blue”
android:layout_width=”0dip”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:layout_weight=”1″/>
<TextView
android:background=”@drawable/yellow”
android:layout_width=”0dip”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:layout_weight=”1″/>
</LinearLayout>
注意这里四个TextView 的权重都设为1,因此将平均分配大小。使用权重的一个基本算法,LinearLayout 剩余的空间有所有有“权重”的View按照其权值按比例分配大小。
补充:移动开发 , Android ,