[Android应用开发]-(11)使用JPCT-AE 3D框架实现旋转的立方体(附效果图及源码)
效果图:
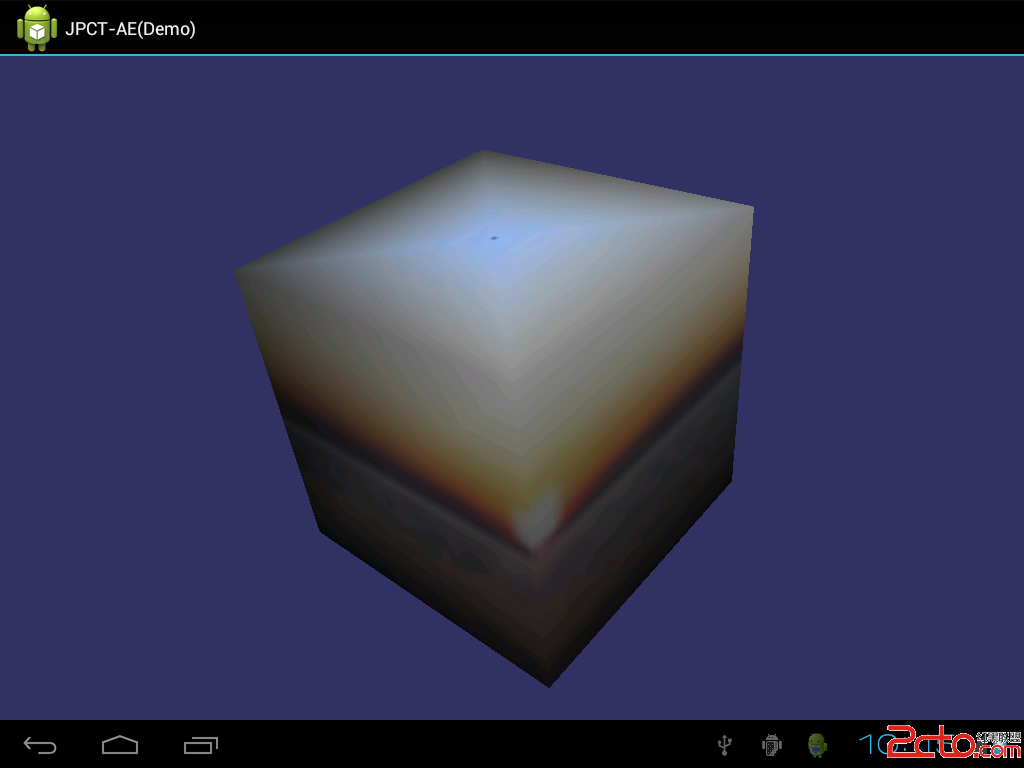
源码:
[java]
package org.winplus.hw;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGL10;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLDisplay;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.opengl.GLSu易做图ceView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import com.threed.jpct.Camera;
import com.threed.jpct.FrameBuffer;
import com.threed.jpct.Light;
import com.threed.jpct.Logger;
import com.threed.jpct.Object3D;
import com.threed.jpct.Primitives;
import com.threed.jpct.RGBColor;
import com.threed.jpct.SimpleVector;
import com.threed.jpct.Texture;
import com.threed.jpct.TextureManager;
import com.threed.jpct.World;
import com.threed.jpct.util.BitmapHelper;
import com.threed.jpct.util.MemoryHelper;
/**
*
* 一个简单的例子。比起展示如何写一个正确的android应用它更着重于展示如何使用JPCT-AE这个3D游戏框架。
* 它包含了Activity类去处理pause和resume等方法
*
* @author tangcheng_ok
*
*/
public class JPCT_AE_Activity extends Activity {
// HelloWorld对象用来处理Activity的onPause和onResume方法
private static JPCT_AE_Activity master = null;
// GLSu易做图ceView对象
private GLSu易做图ceView mGLView;
// 类MyRenderer对象
private MyRenderer renderer = null;
// 当JPCT渲染背景时FrameBuffer类提供了一个缓冲,它的结果本质上是一个能显示或者修改甚至能进行更多后处理的图片。
private FrameBuffer fb = null;
// World类是JPCT时最重要的一个类,它好像胶水一样把事物"粘"起来。它包含的对象和光线定义了JPCT的场景
private World world = null;
// 类似java.awt.*中的Color类
private RGBColor back = new RGBColor(50, 50, 100);
private float touchTurn = 0;
private float touchTurnUp = 0;
private float xpos = -1;
private float ypos = -1;
/*
* Object3D类是一个三维对象,千万不要傻呼呼的认为它与java.lang.Object类似。
* 一个Object3D对象作为一个实例被添加到在渲染的World对象中。Object3D在World中一次添加一个实例
* ,他们可能被联系起作为孩子/父母来在他们中建立一个制度.
* 人体模型当然也能应用在以上的规则中。他们常常不加到一个World实例中,而是绑定到其它对象中(人体模型或非人体模型)。有些方法
* 在这个类中需要一个实例添加到一个World实例中(用World.addObject()方法可以实现)。
*/
private Object3D cube = null;
// 每秒帧数
private int fps = 0;
// 光照类
private Light sun = null;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Logger类中 jPCT中一个普通的用于打印和存储消息,错误和警告的日志类。 每一个JPCT生成的消息将被加入到这个类的队列中
Logger.log("onCreate");
// 如果本类对象不为NULL,将从Object中所有属性装入该类
if (master != null) {
copy(master);
}
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 实例化GLSu易做图ceView
mGLView = new GLSu易做图ceView(this);
// 使用自己实现的 EGLConfigChooser,该实现必须在setRenderer(renderer)之前
// 如果没有setEGLConfigChooser方法被调用,则默认情况下,视图将选择一个与当前android.view.Su易做图ce兼容至少16位深度缓冲深度EGLConfig。
mGLView.setEGLConfigChooser(new GLSu易做图ceView.EGLConfigChooser() {
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display) {
// Ensure that we get a 16bit framebuffer. Otherwise, we'll fall
// back to Pixelflinger on some device (read: Samsung I7500)
int[] attributes = new int[] { EGL10.EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 16,
EGL10.EGL_NONE };
EGLConfig[] configs = new EGLConfig[1];
int[] result = new int[1];
egl.eglChooseConfig(display, attributes, configs, 1, result);
return configs[0];
}
});
// 实例化MyRenderer
renderer = new MyRenderer();
// 设置View的渲染器,同时启动线程调用渲染,以至启动渲染
mGLView.setRenderer(renderer);
// 设置一个明确的视图
setContentView(mGLView);
}
// 重写onPause()
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mGLView.onPause();
}
// 重写onResume()
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mGLView.onResume();
}
// 重
补充:移动开发 , Android ,