C++死锁解决心得
一、 概述
C++多线程开发中,容易出现死锁导致程序挂起的现象。
解决步骤分为三步:
1、检测死锁线程。
2、打印线程信息。
3、修改死锁程序。
二、 程序示例
VS2005创建支持MFC的win32控制台程序。
代码见示例代码DeadLockTest.cpp。
[cpp]
// DeadLockTest.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "DeadLockTest.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
// The one and only application object
CWinApp theApp;
using namespace std;
CRITICAL_SECTION cs1;
CRITICAL_SECTION cs2;
CRITICAL_SECTION csprint;
//初始化关键代码段
void InitMyCriticalSection();
//删除关键代码段
void DeleteMyCriticalSection();
//打印信息
void PrintString(const CString& strInfo);
DWORD WINAPI Thread1(LPVOID lpParameter);
DWORD WINAPI Thread2(LPVOID lpParameter);
int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR* argv[], TCHAR* envp[])
{
int nRetCode = 0;
// initialize MFC and print and error on failure
if (!AfxWinInit(::GetModuleHandle(NULL), NULL, ::GetCommandLine(), 0))
{
// TODO: change error code to suit your needs
_tprintf(_T("Fatal Error: MFC initialization failed\n"));
nRetCode = 1;
return nRetCode;
}
//初始化关键代码段
InitMyCriticalSection();
//创建线程
HANDLE hThread1 = CreateThread(NULL, 0, Thread1, NULL, 0, NULL);
HANDLE hThread2 = CreateThread(NULL, 0, Thread2, NULL, 0, NULL);
//等待线程结束
WaitForSingleObject(hThread1, INFINITE);
WaitForSingleObject(hThread2, INFINITE);
//关闭线程句柄
CloseHandle(hThread1);
CloseHandle(hThread2);
//释放关键代码段
DeleteMyCriticalSection();
return nRetCode;
}
void InitMyCriticalSection()
{
InitializeCriticalSection(&cs1);
InitializeCriticalSection(&cs2);
InitializeCriticalSection(&csprint);
}
void DeleteMyCriticalSection()
{
DeleteCriticalSection(&cs1);
DeleteCriticalSection(&cs2);
DeleteCriticalSection(&csprint);
}
DWORD WINAPI Thread1(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&cs1);
Sleep(500);
EnterCriticalSection(&cs2);
PrintString(_T("Thread1"));
LeaveCriticalSection(&cs2);
LeaveCriticalSection(&cs1);
}
return 1;
}
DWORD WINAPI Thread2(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&cs2);
Sleep(500);
EnterCriticalSection(&cs1);
PrintString(_T("Thread2"));
LeaveCriticalSection(&cs1);
LeaveCriticalSection(&cs2);
}
return 1;
}
void PrintString(const CString& strInfo)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&csprint);
wcout<<(const TCHAR*)strInfo<<endl;
LeaveCriticalSection(&csprint);
}
运行DeadLockTest.exe,程序挂起。
三、 死锁检测
检测工具见《Windows核心编程》,第9章9.8.6节LockCop检测工具。
LockCop可使用vs2010编译成功。
备注:该工具使用了Windows Vista/ 7提供的WCT API,故需要在Windows Vista/ 7系统运行LockCop检测工具。
检测,挂起的DeadLockTest.exe,得到线程信息。
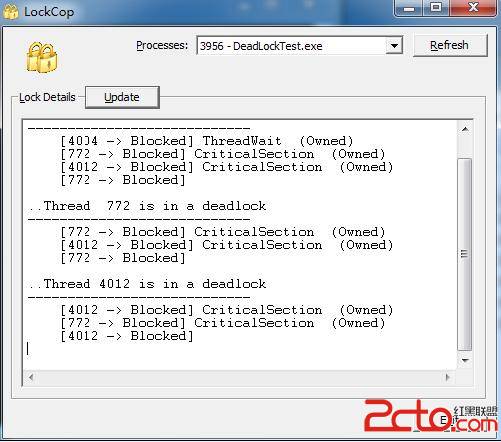
检测到程序挂起由死锁引起。
线程4014:等待线程772、线程4012完成。
线程772:拥有关键代码段A,等待关键代码段B(被线程4012拥有)。
线程4012:拥有关键代码段B,等待关键代码段A(被线程772拥有)。
线程772与4012互相等待,程序发生死锁现象。
四、 打印信息
为了便于查找问题,我们加上线程打印信息。
打印线程名称、线程ID以及关键代码段进入信息。
[cpp]
DWORD WINAPI Thread1(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
CString strThreadID = _T("");
strThreadID.Format(_T("%d"), GetCurrentThreadId());
CString strPrintInfo = _T("");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&cs1);
strPrintInfo = _T("");
strPrintInfo += _T("Thread1 ");
strPrintInfo += strThreadID;
strPrintInfo += _T(" EnterCriticalSection(&cs1)");
PrintString(strPrintInfo);
Sleep(500);
EnterCriticalSection(&cs2);
strPrintInfo = _T("");
strPrintInfo += _T("Thread1 ");
strPrintInfo += strThreadID;
strPrintInfo += _T(" EnterCriticalSection(&cs2)");
PrintString(strPrintInfo);
LeaveCriticalSection(&cs2);&
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,