C++的私有继承、公有继承和保护继承
[cpp]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
protected:
int test;
public:
Animal(){ test = 0; cout << "animal init...\n";}
void eat(){cout << "Animal eat..." << endl;}
};
class Giraffe: private Animal
{
public:
Giraffe(){cout << "giraffe init...\n";}
void StrechNeck(double)
{
eat();
cout << "test: "<<test << endl;
cout << "strech neck \n"<<endl;
}
};
class Cat: public Animal
{
public:
Cat(){cout << "cat init...\n";}
// void eat(){cout << "cat eat ...\n";}
void Meaw(){
eat();
cout << "meaw\n";}
};
void Func(Animal& an)
{
an.eat();
}
int main()
{
Cat dao;
Giraffe gir;
Func(dao);
dao.Meaw();
cout << "==========================\n";
gir.StrechNeck(12);
// Func(gir);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
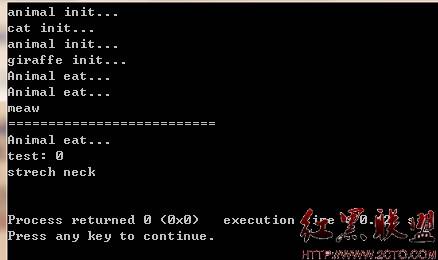
总结:
1. 不管是私有继承还是公有继承都无法访问父类的私有成员;
2. 公有继承的子类对象,可以直接访问父类的protected和public的成员,就如同访问自己的成员一样;
3. 私有继承的子类对象,不能直接访问父类的任何成员;
4. 私有继承的子类对象,如果想要访问父类成员,只能通过子类的成员函数来访问父类的成员,就如同父类成员函数访问自己的成员(当然,父类的private成员无法访问)。
5. 保护继承与私有继承类似,继承之后的类相对于父类是独立的;其类对象,在公开场合无法使用基类的成员,也只能通过自己的成员函数来访问父类的protected和public成员。
补充:软件开发 , C++ ,